Anatomy
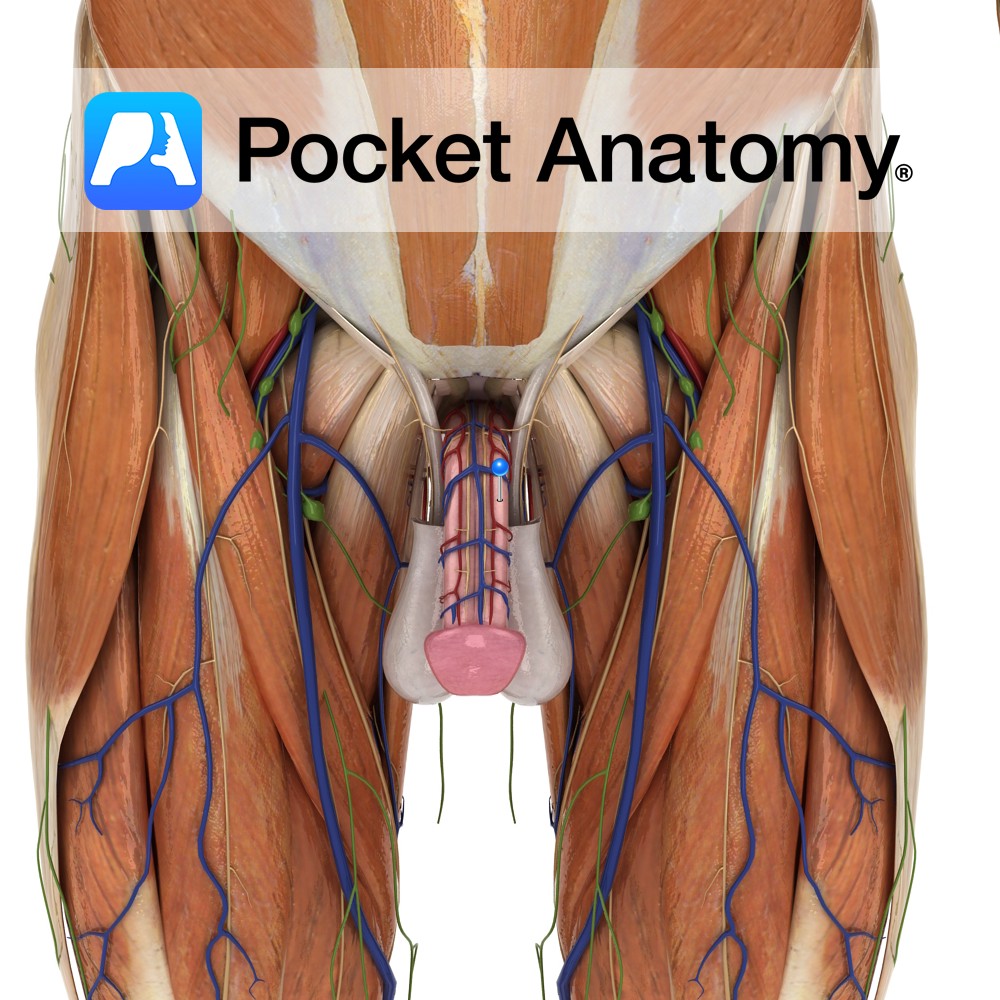
There are 3 cylindrical strips of expandable/inflatable/erectile tissue along length of penis; 2 corpus cavernosum side by side and dorsal to 1 (smaller) corpus spongiosum (central and ventral, expanded at proximal end into bulb and distal into glans, and through which urethra courses). Corpus cavernosum starts at pubic bone, left and right end by joining at glans of spongiosum (which moulds/molds around and covers them).
Physiology
90% of blood in erect penis is in the 2 corpus cavernosum (or corpora cavernosa ie plural); corpus spongiosum about 7%. Nitric oxide and cyclic guanosine monophosphate cGMP mediate erection (influenced/stimulated by testosterone). Pressure flaccid penis 10-15mm, erect 120mm. Penile volume increases 3-fold to 120ml.
Clinical
Penile fracture (rare) is a rupture of one or both corpus cavernosum, leading to bending and rupture of tunica albuginea (very strong, but thinned from about 2.5mm to 0.5mm during erection); urethra rarely (3%) ruptured in process. Surgical repair effective.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?