Anatomy
Origin:
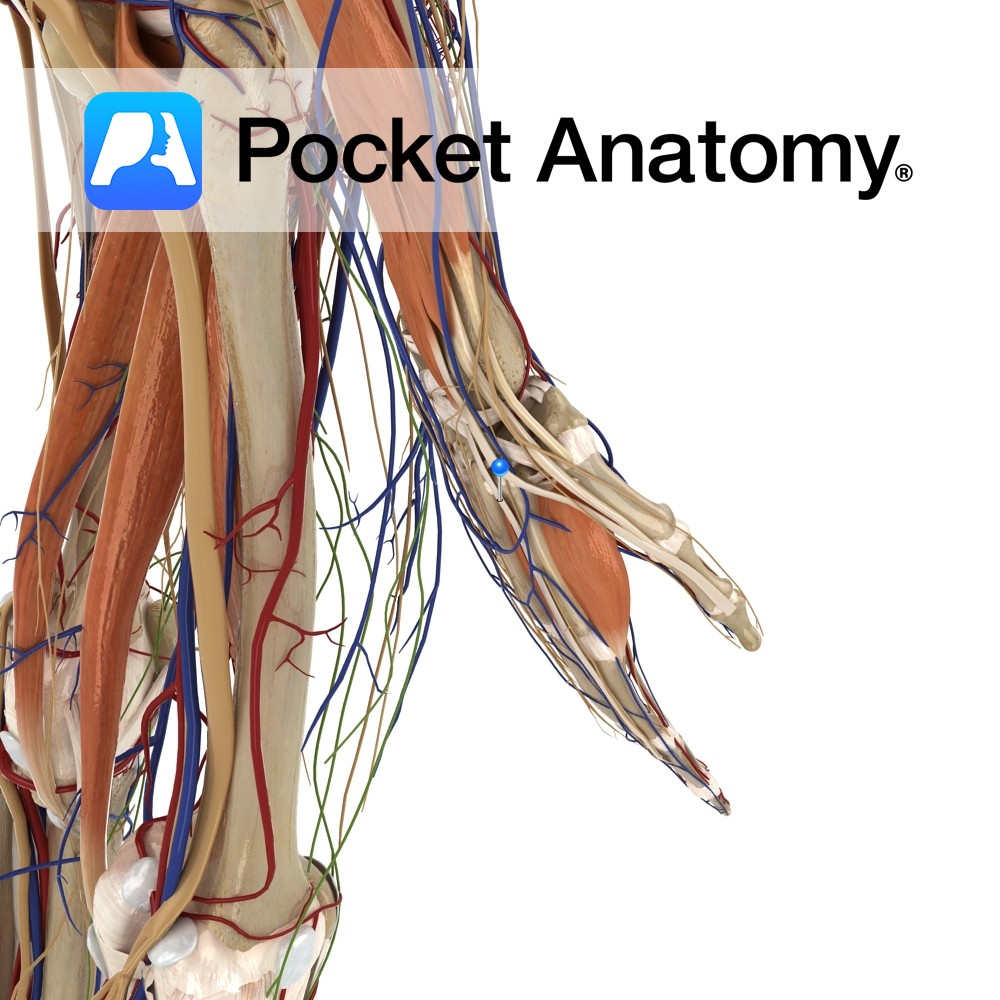
Junction of middle and distal thirds of ulna and adjacent interosseous membrane.
Insertion:
Extensor hood of index finger.
Key Relations:
The tendon of extensor indicis passes under the extensor retinaculum in a compartment with extensor digitorum.
One of the six muscles in the deep posterior compartment of the forearm.
Functions
-Extends index finger at metacarpophalangeal joint.
-Extends index fingers interphalangeal joints (with lumbricals and Interossei)
-Helps adduct the index finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint
-Helps extend hand at wrist
e.g. as in pointing with your index finger..
Supply
Nerve Supply:
Posterior interosseous nerve (C7,C8) (continuation of deep branch of the radial nerve).
Blood Supply:
Posterior interosseous artery.
Clinical
The index finger is extended by the action of two muscles extensor digitorum and extensor indicis. Due to these dual extensors the tendon of extensor indicis may be used for tendon transfer or grafting, while still allowing extension of the index finger. One example of this is the use of a tendon transfer procedure to repair a ruptured extensor pollicis longus tendon and restore its function.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?