Anatomy
Course
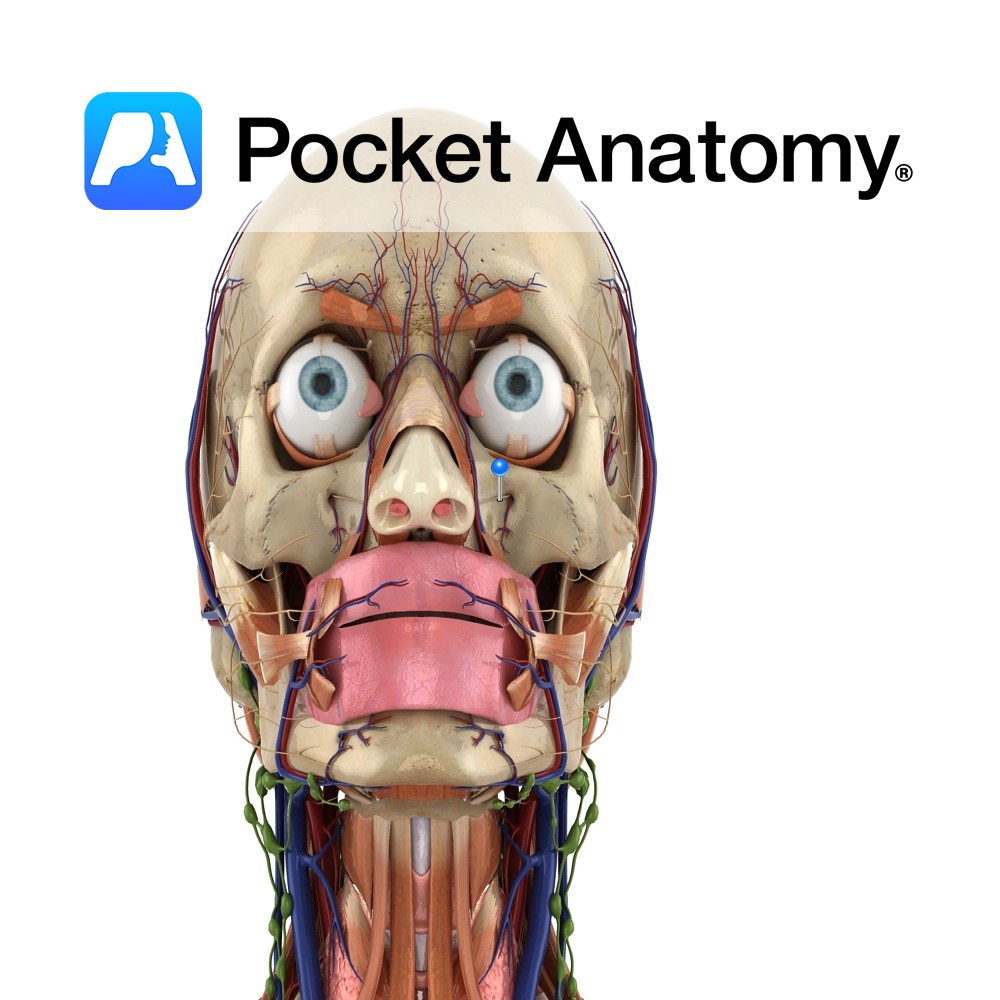
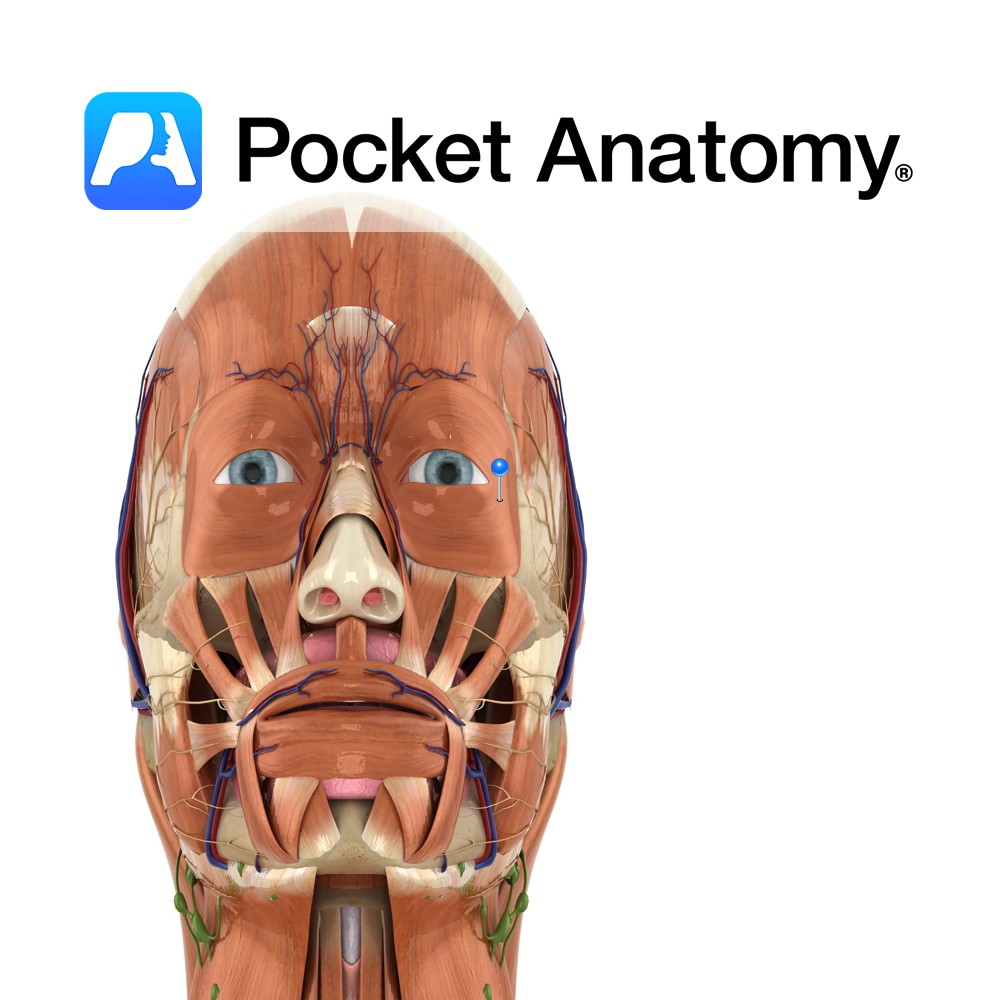
The maxillary nerve (V2) is one of the branches of the trigeminal nerve (V). It branches from the trigeminal nerve whilst it is still in the middle cranial fossa and then exits the inside of the skull through the foramen rotundum. From here, it crosses the pterygopalatine fossa and enters the eye socket. It gives off a number of branches along its course.
Supply
The maxillary nerve is a purely sensory nerve. It and its branches provide sensory innervation to the maxillary, sphenoid and ethmoid sinuses, as well as some of the skin on the front of the face and the upper oral cavity.
Clinical
Damage to the maxillary nerve (V2) or even the trigeminal nerve (V) will result in a loss of sensation over its distribution in the face.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?


.jpg)