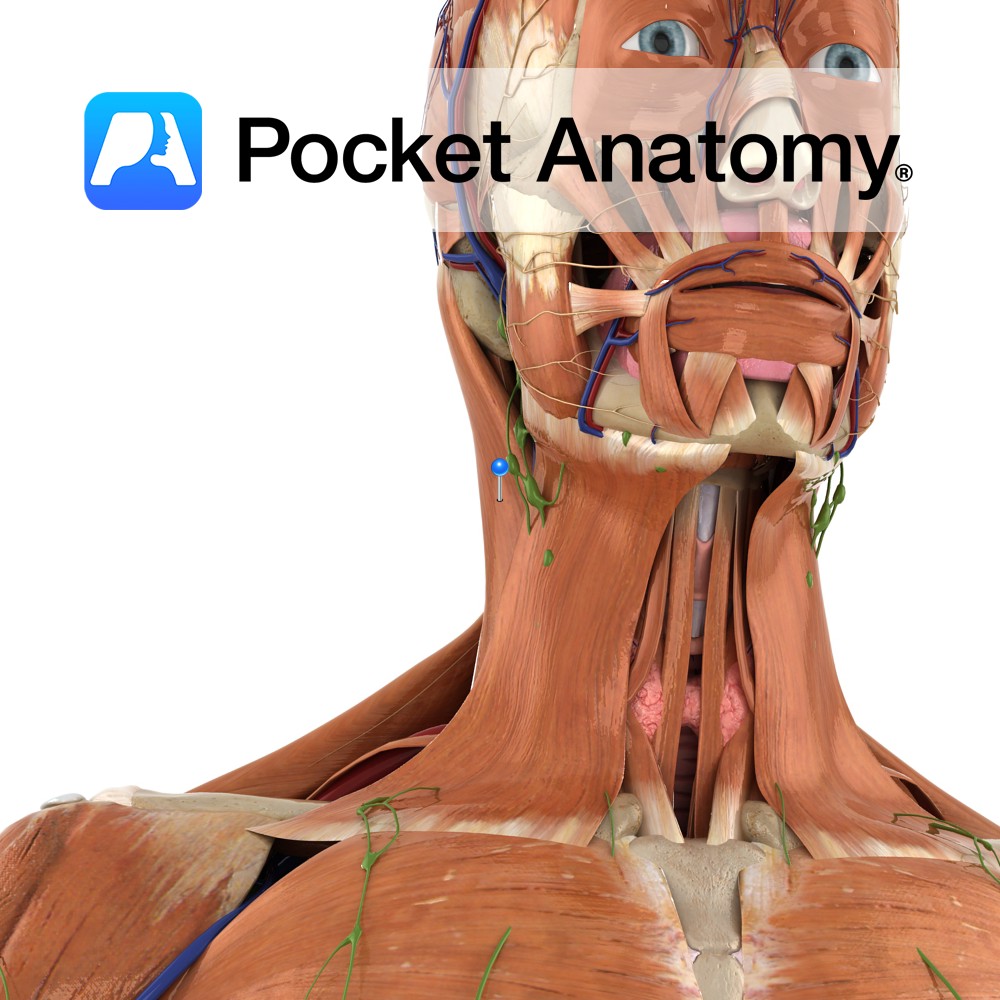
Anatomy
Origin:
Sternal head: Upper part of anterior surface of manubrium of sternum.
Clavicular head: Superior surface of medial one third of the clavicle.
Insertion:
Sternal head: Lateral half of superior nuchal line.
Clavicular head: Lateral surface of mastoid process.
Key Relations:
-Posterior edge forms anterior border of posterior triangle of the neck.
-Anterior edge forms posterior border of anterior triangle of the neck.
Functions
-Acting unilaterally, tilts head towards shoulder on same side e.g. holding the phone between your ear and shoulder and rotates head to turn face to opposite side e.g. looking over your shoulder.
-Acting bilaterally, tilts the head forward onto thorax e.g. looking at the floor..
Supply
Nerve Supply:
Accessory nerve (CN 11) and anterior rami of C2 and C3.
Blood Supply:
–Occipital artery
-Superior thyroid artery.
Clinical
Torticollis is a postural deformity of the neck due to spasms of the sternocleidomastoid that can develop in adults. It can cause pain and turning and tilting of the head. Congenital torticollis can occur in infants due the development of a fibrous tissue tumour in the muscle in utero.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?


.jpg)