PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
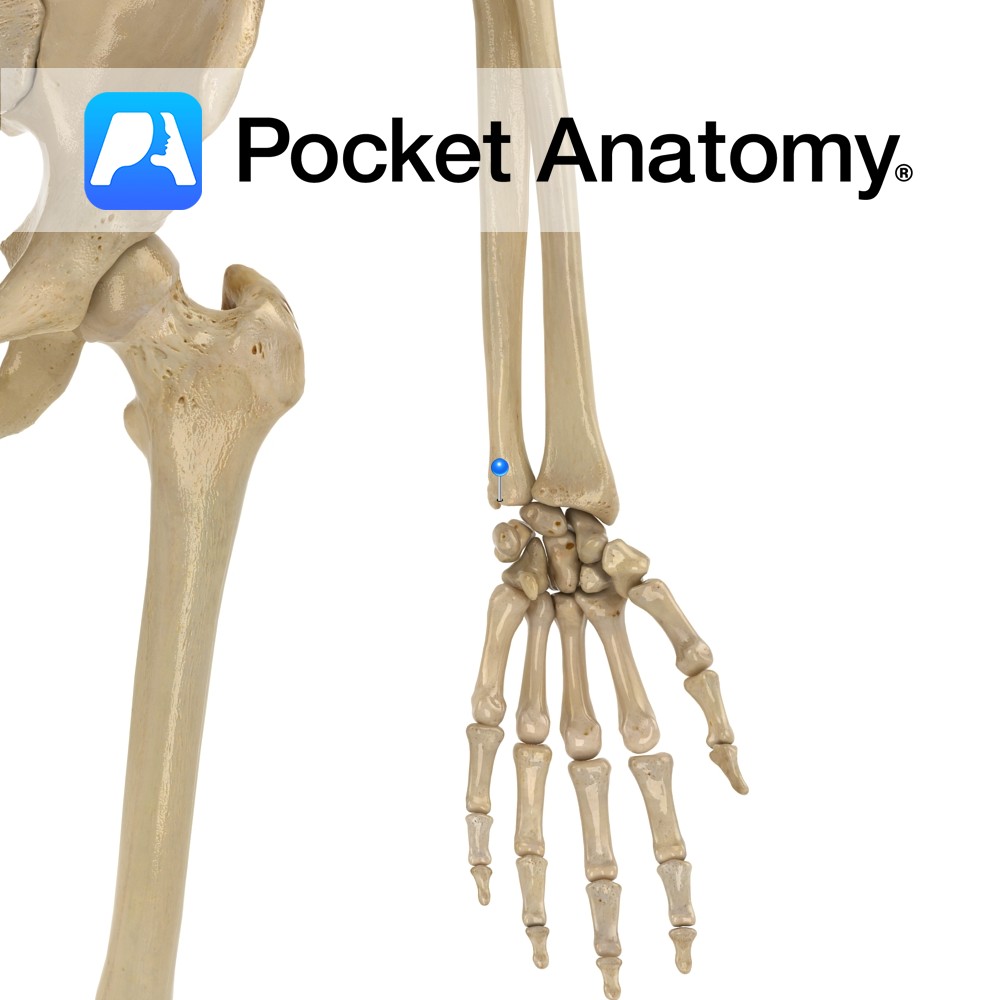
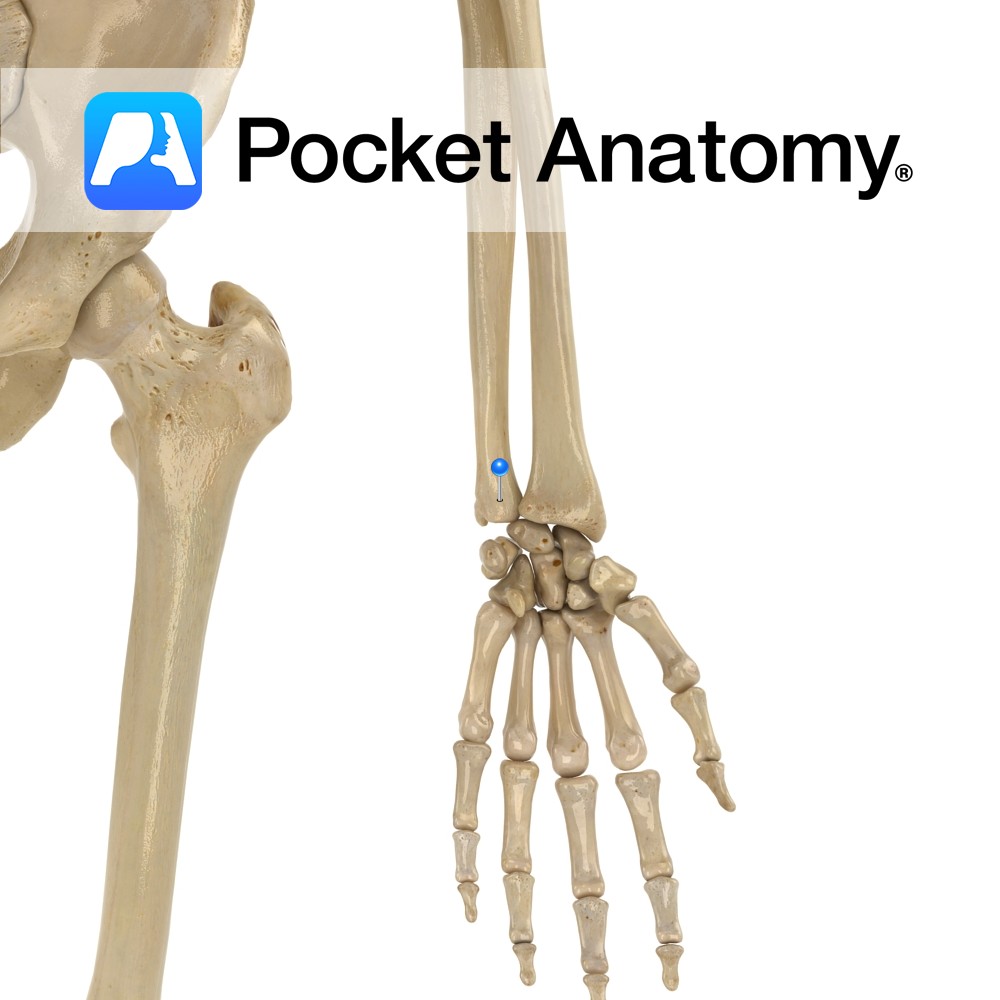
Anatomy Bulge posteriorly from medial (little finger side) lower extremity, giving attachment to ulnar collateral ligament of wrist (there are ulnar collateral ligaments of elbow, wrist, thumb.) Smaller, more superior/proximal than radial styloid. Clinical Easily visible dorsal/posterior bump proximal to wrist. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
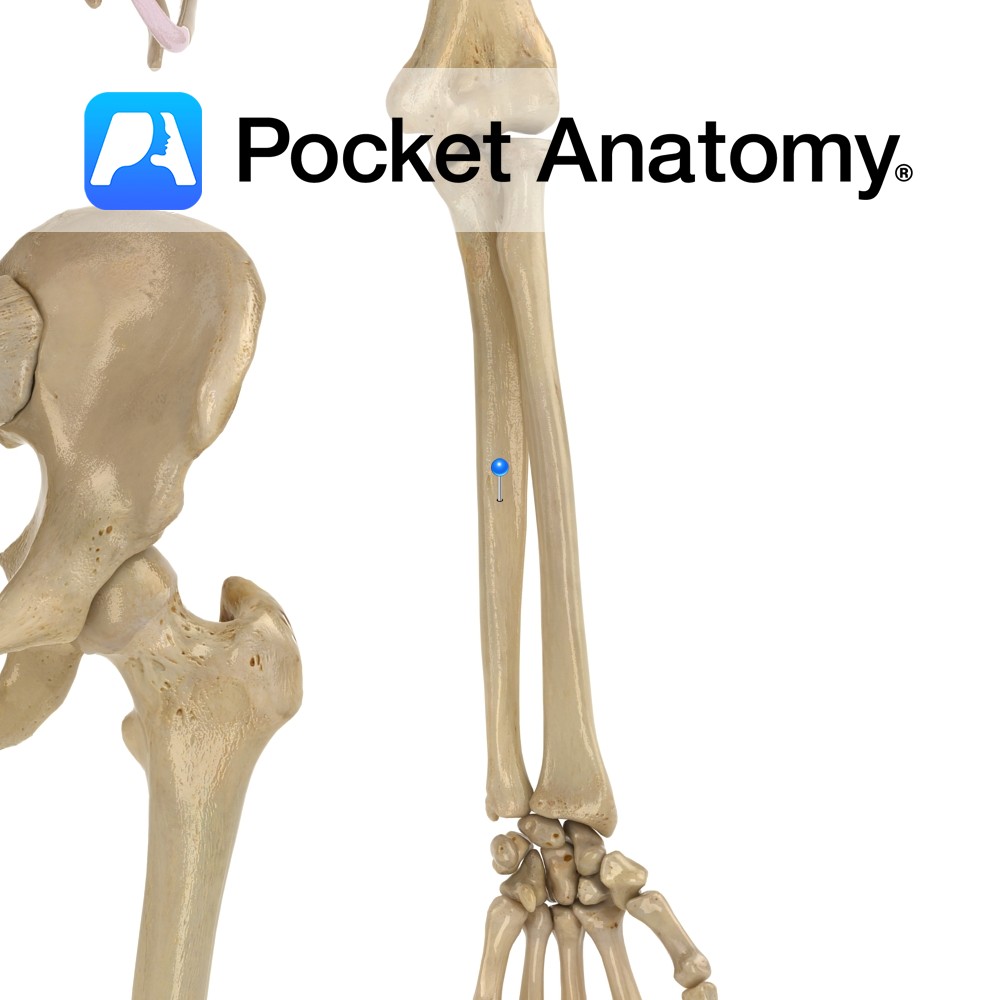
Anatomy Ulna and radius shafts joined (syndesmosis joint – allows slight movement) by interosseous membrane along their lengths. Clinical Nightstick fracture; isolated fracture, usually due to direct trauma. Vignette Desmos (Greek); band. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy The radial head articulates with (rolls over) the radial notch of ulna, manifest as pronation and supination. At the lower end of the forearm, the ulnar head articulates with the ulnar notch of the radial head. Clinical Radial head is proximal and articulates with a notch on the ulna; ulnar head is distal and
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
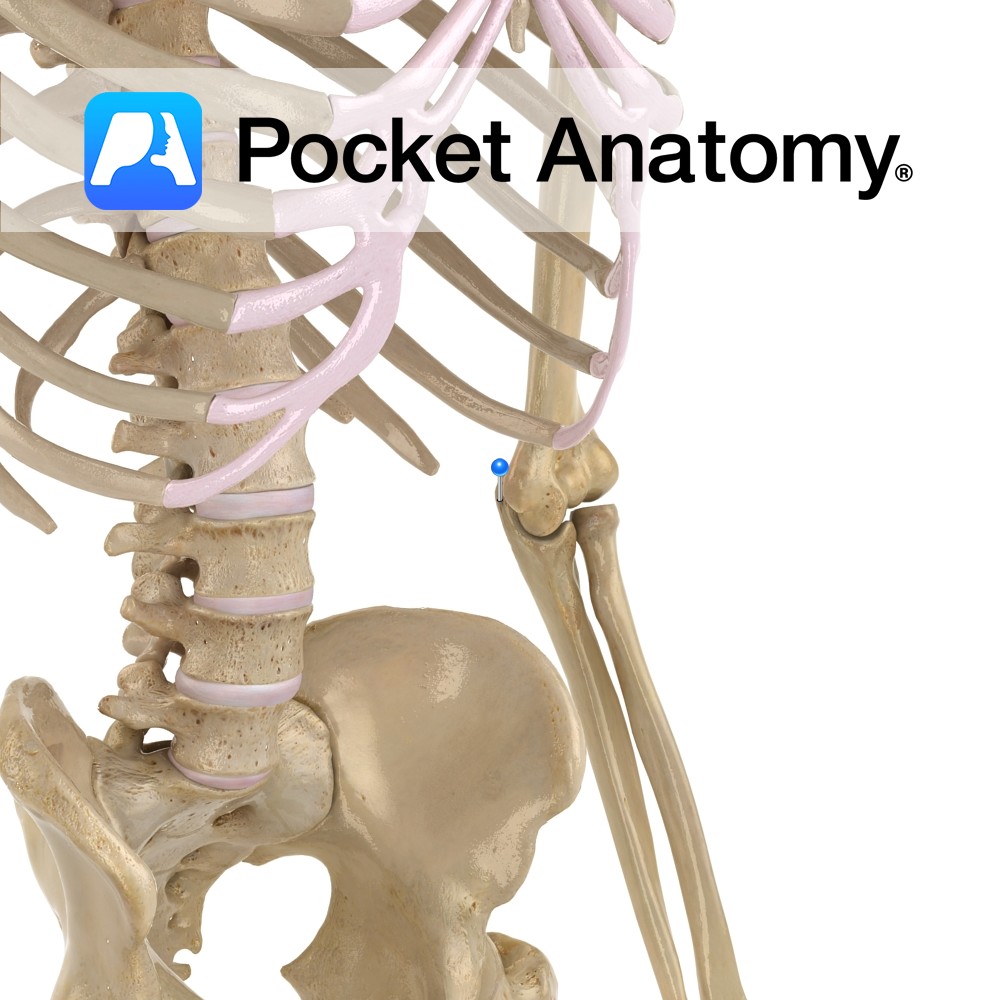
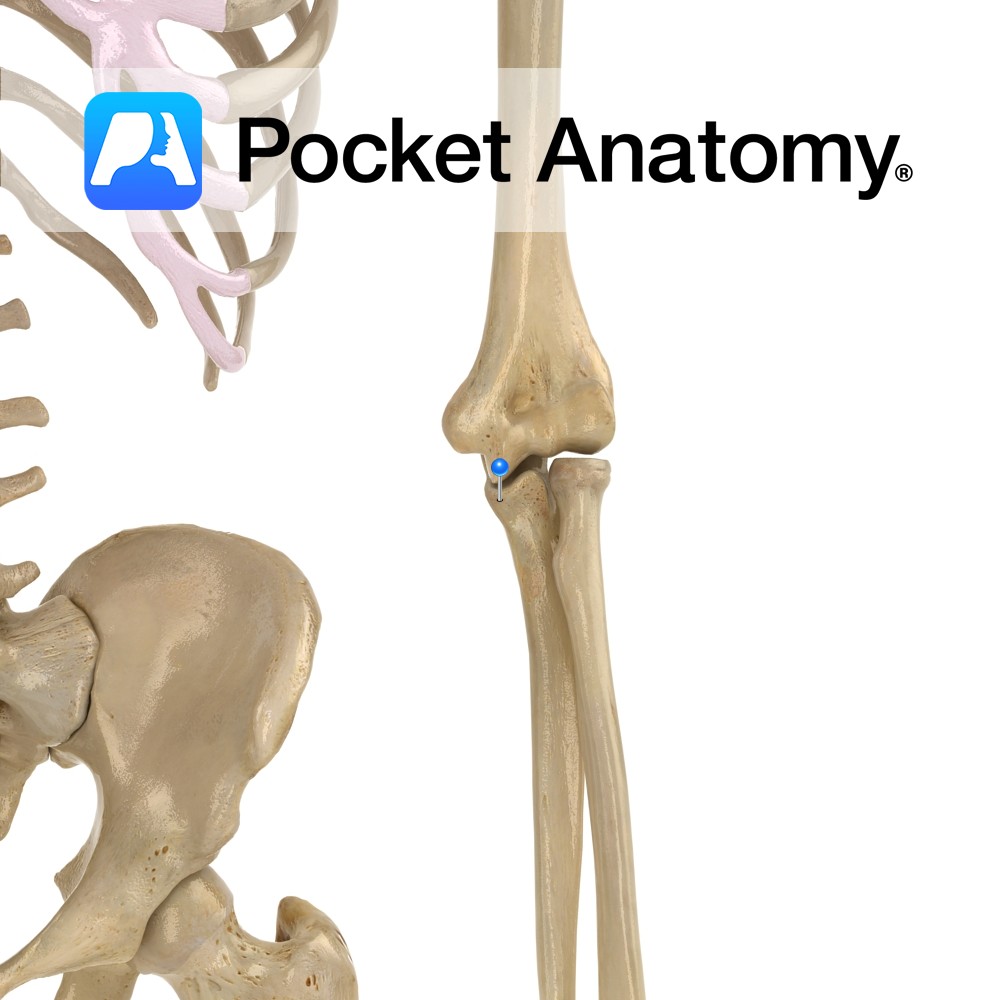
Anatomy Curved bulge upper end ulna, sits, when elbow extended, in olecranon fossa at back of bottom of humerus, lending significant bony strength, stability and movement limitation (stopping hyperextension). Attachments; triceps brachii, posterior and ulnar collateral ligaments. Clinical Back of olecranon process covered by bursa, just subcutaneous; bursitis in trauma, infection, pressure, rheumatoid arthritis, gout.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Articulates down with articular disc between it and wrist joint, and laterally with the ulnar notch of the radius (pivot joint). Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
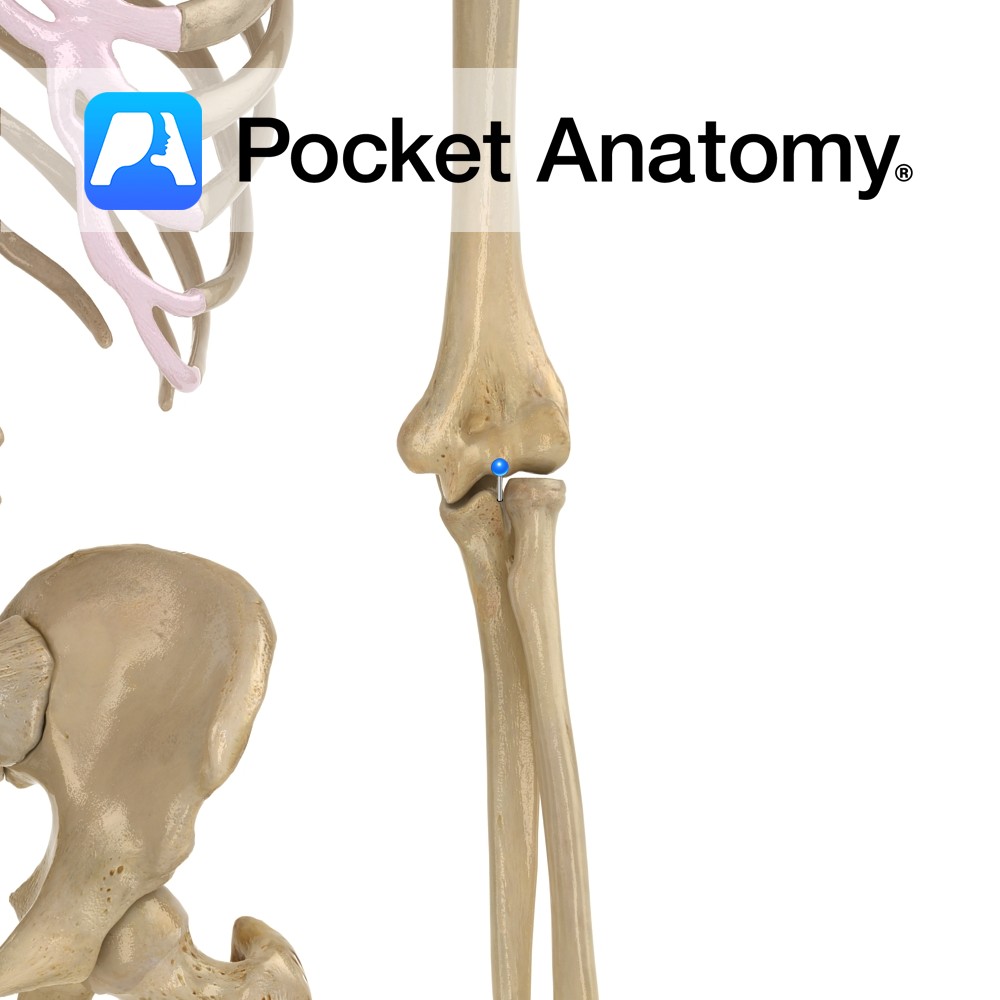
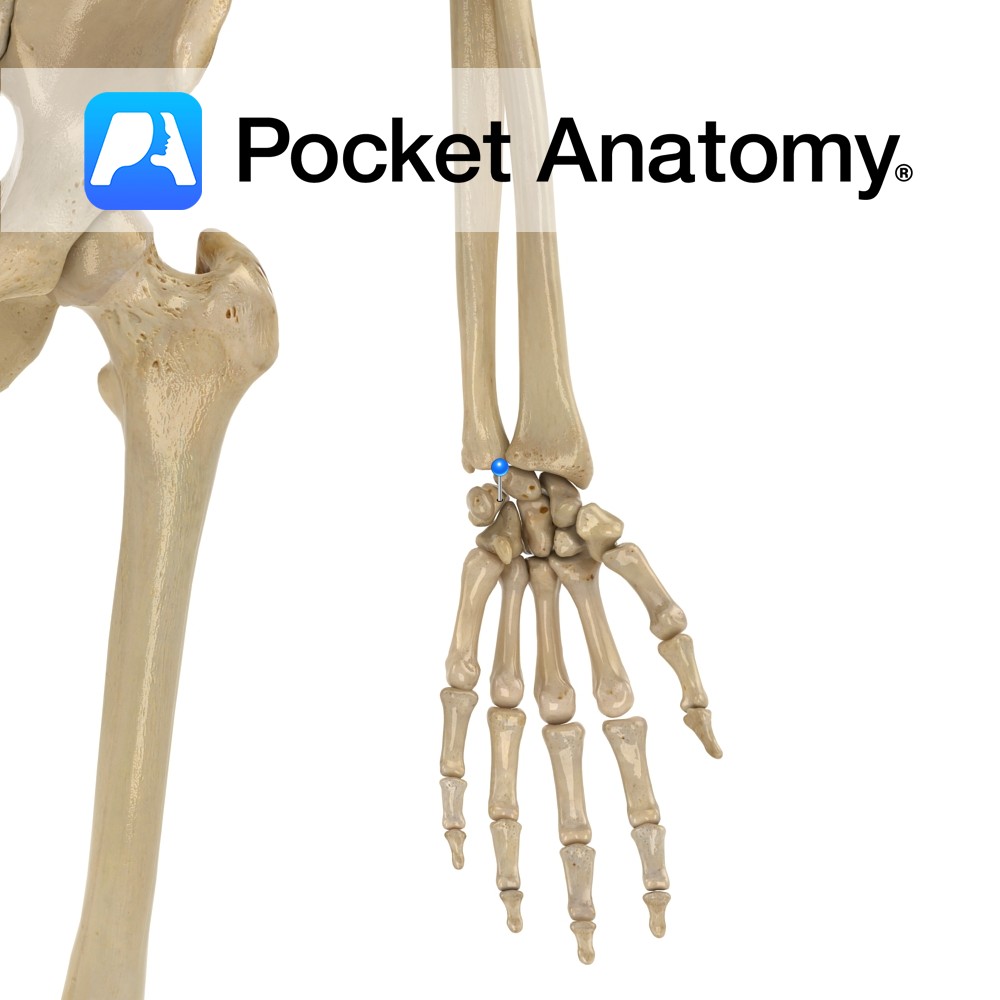
Anatomy Separated from olecranon by trochlear notch, sits in coronoid fossa of humerus, just above trochlea, when elbow bent (elbow flexed). The radial notch is at its lateral edge. Attachments; brachialis, parts of flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus, pronator teres, sometimes flexor pollicis longus. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Small finger side of nearer row of carpal bones, pyramidal shape. Articulates out with lunate, down with hamate, in front (palmar) with pisiform. On ulnar side but does not articulate with it. Clinical The palmar (anterior) aspect of the carpus is concave and, covered with the flexor retinaculum (ligament), forms the carpal tunnel. Interested
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: The trigeminal motor nucleus is located in the mid pons tegmentum and the trigeminal sensory nucleus extends the length of the brain stem and upper cervical cord. Its subnuclei include the principal sensory nucleus located in the pontine tegmentum, the mesencephalic nucleus extending into the midbrain and the spinal nucleus extending through the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Medial head: Posterior surface of the humerus inferior to the radial groove. Lateral head: Posterior surface of the humerus superior to the radial groove. Long head: Infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula. Insertion: Olecranon process of the ulna and deep fascia of the forearm. Key Relations: -Medial heads lies posterior to the long and
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Long head: Infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula. Lateral head: Posterior surface of the humerus superior to the radial groove. Medial head: Posterior surface of the humerus inferior to the radial groove. Insertion: Olecranon process of the ulna and deep fascia of the forearm. Key Relations: -Long head lies between teres minor and teres
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)