Anatomy
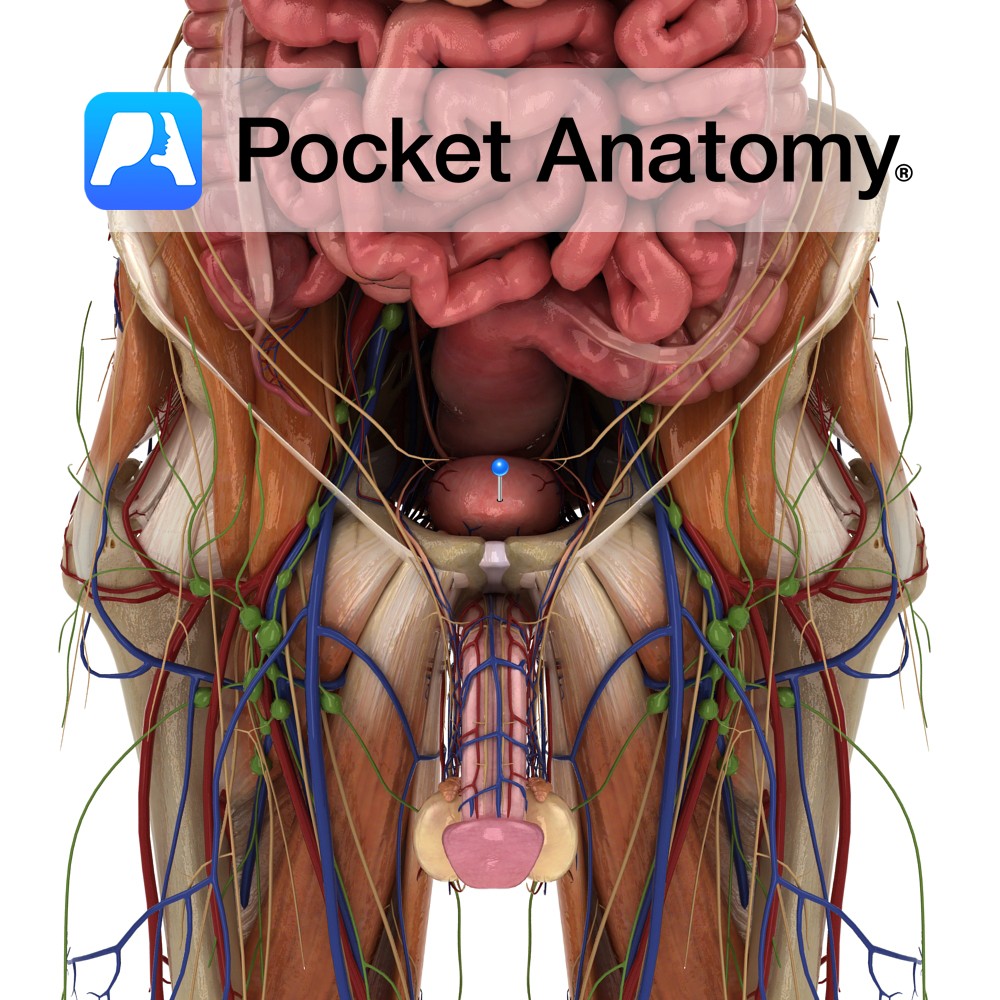
Hollow distensible muscular organ, extra-peritoneal on pelvic floor behind pubic symphysis; 300-600 mls capacity; urine enters through ureteral openings 2-3 cms apart in posterior wall, is extruded through internal urethral orifice below (trigone the area thus bounded); dome, posterior surface covered with peritoneum; neck fixed by true ligaments of pelvis and fascia; body supported by external urethral sphincter and perineal membrane below, obturator internus muscles either side; multidirectional muscular fibres in wall (detrusor muscle) suited for shrinking of bladder; neck (contiguous with prostate in males) acts as internal sphincter; primarily supplied by internal iliac (hypogastric) arteries – superior/inferior vesical arteries; accompanying veins drain to internal iliac.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?