Anatomy
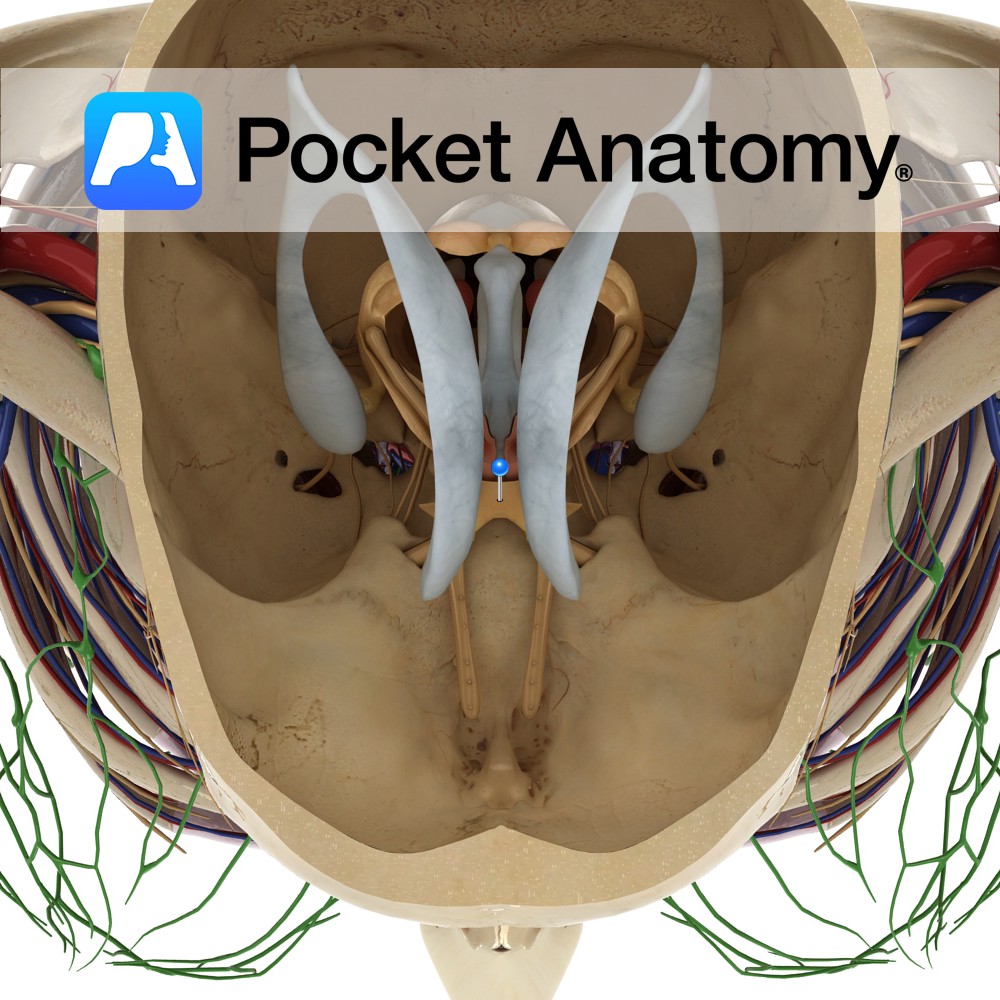
The two optic nerves unite at the optic chiasm which is located at the base of the brain in the interpeduncular cistern. It is situated between the two internal carotid arteries, and the tuber cinereum of the hypothalamus lies posterior to the chiasm.
Blood Supply:
Supplied by the branches of many vessels, particularly the internal carotid, anterior communicating, anterior cerebral and posterior communicating arteries.
Functions
At the chiasm, axons from the nasal portions of each retina undergo decussation and enter the contralateral optic tract, while the axons from the temporal half of the retina remain on the same side.
Clinical
A pituitary tumour pressing on the optic chiasm can lead to bitemporal hemianopia. This results in the loss of vision on the temporal half of the right and left visual fields.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?