Anatomy
Origin:
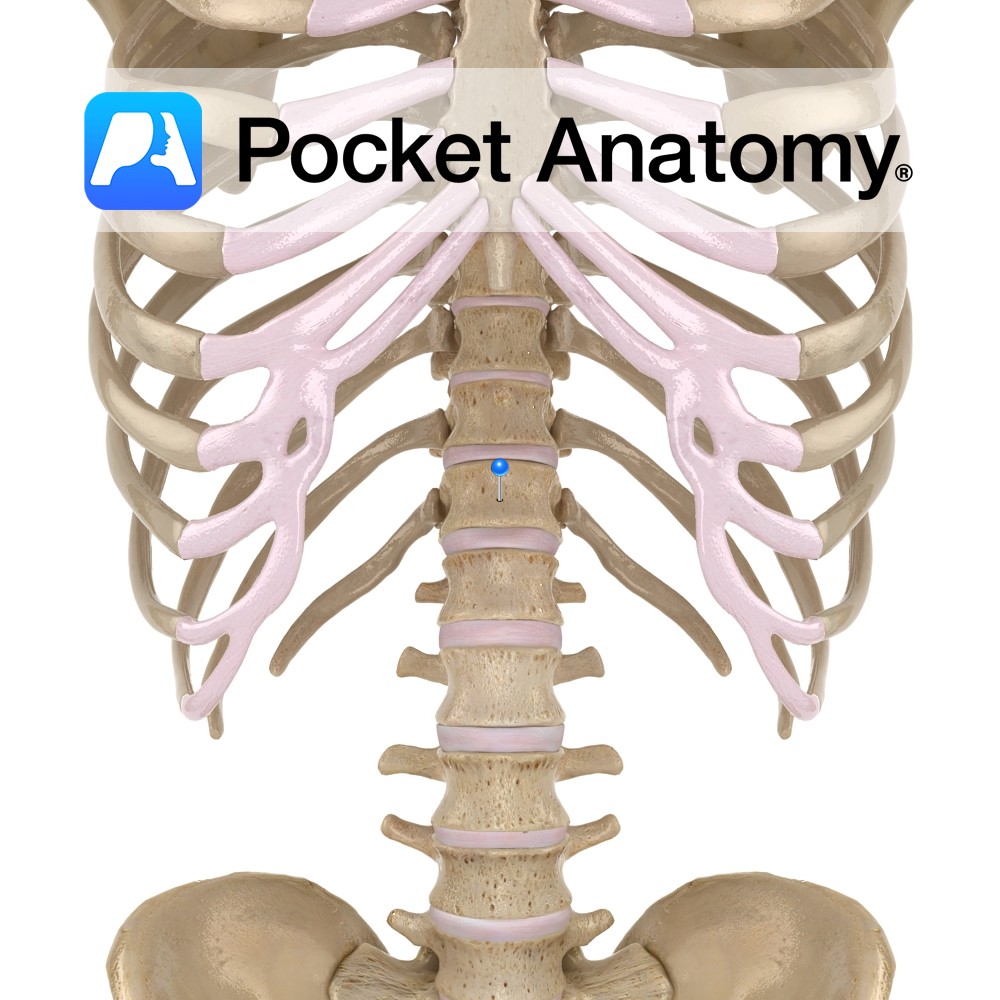
Lower half of ligamentum nuchae and spinous processes of C7 to T4.
Insertion:
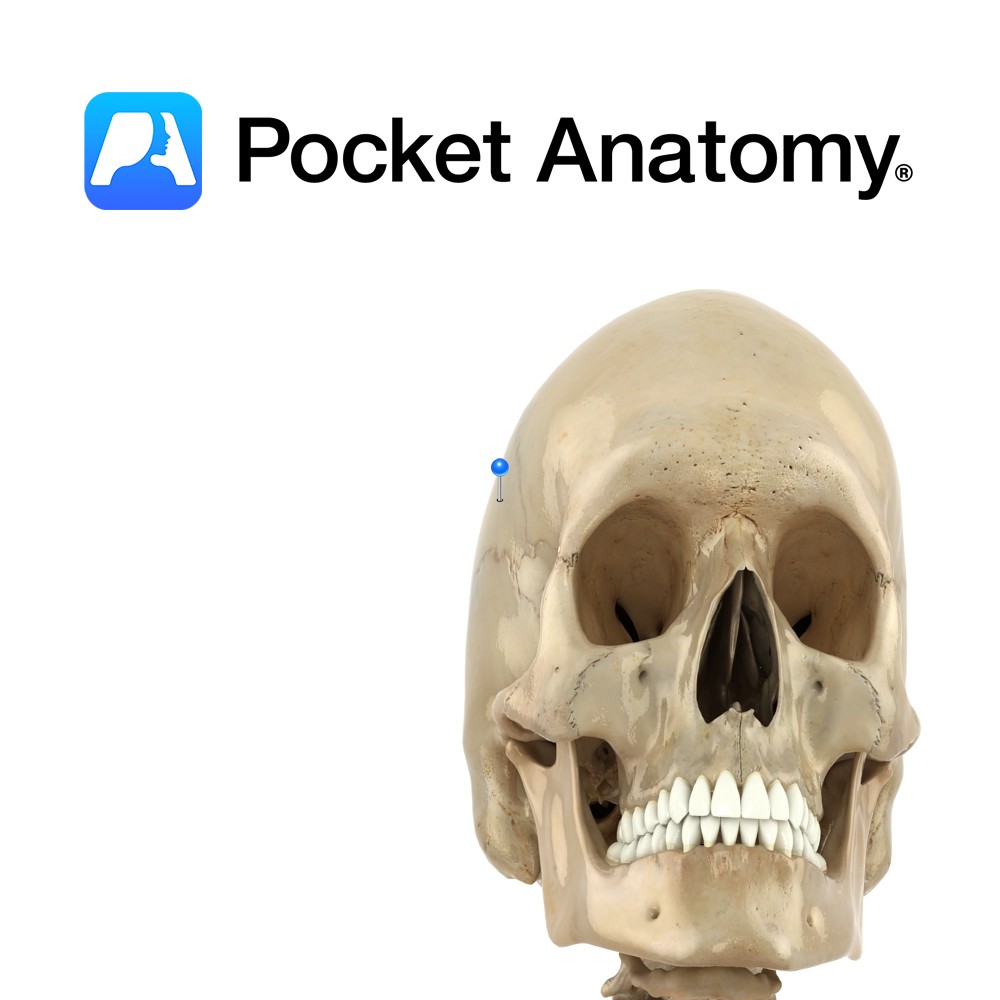
Mastoid process of the temporal bone and just below lateral third of the superior nuchal line on the occipital bone.
Key Relations:
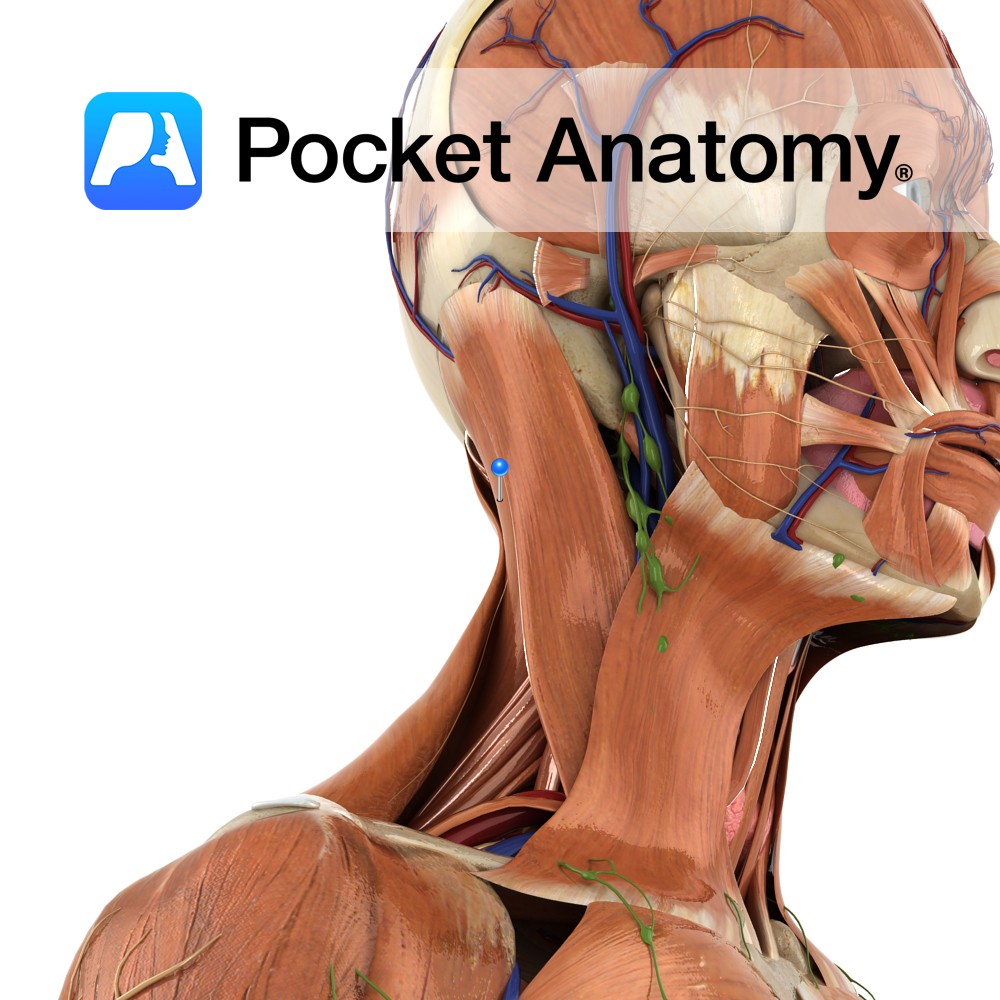
-Superficial to spinalis capitis, semispinalis capitis and longissimus capitis and deep to sternocleidomasteoid.
-Forms part of the floor of the posterior triangle of the neck.
Functions
-Bilaterally, extension of head.
e.g. looking at the sky.
-Unilaterally, lateral rotation and flexion of the head to the same side.
e.g. looking over your shoulder..
Supply
Nerve Supply:
Dorsal rami of middle cervical spinal nerves (C3, C4).
Clinical
Splenius capitis muscle syndrome is one cause of headache. Pain may be experienced in a broad arc from the occiput over the ear, across the zygoma and behind the orbits. Severe cases may result in light sensitivity, nausea and vomiting, mimicking migraine headache and temporal tendonitis.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?


.jpg)