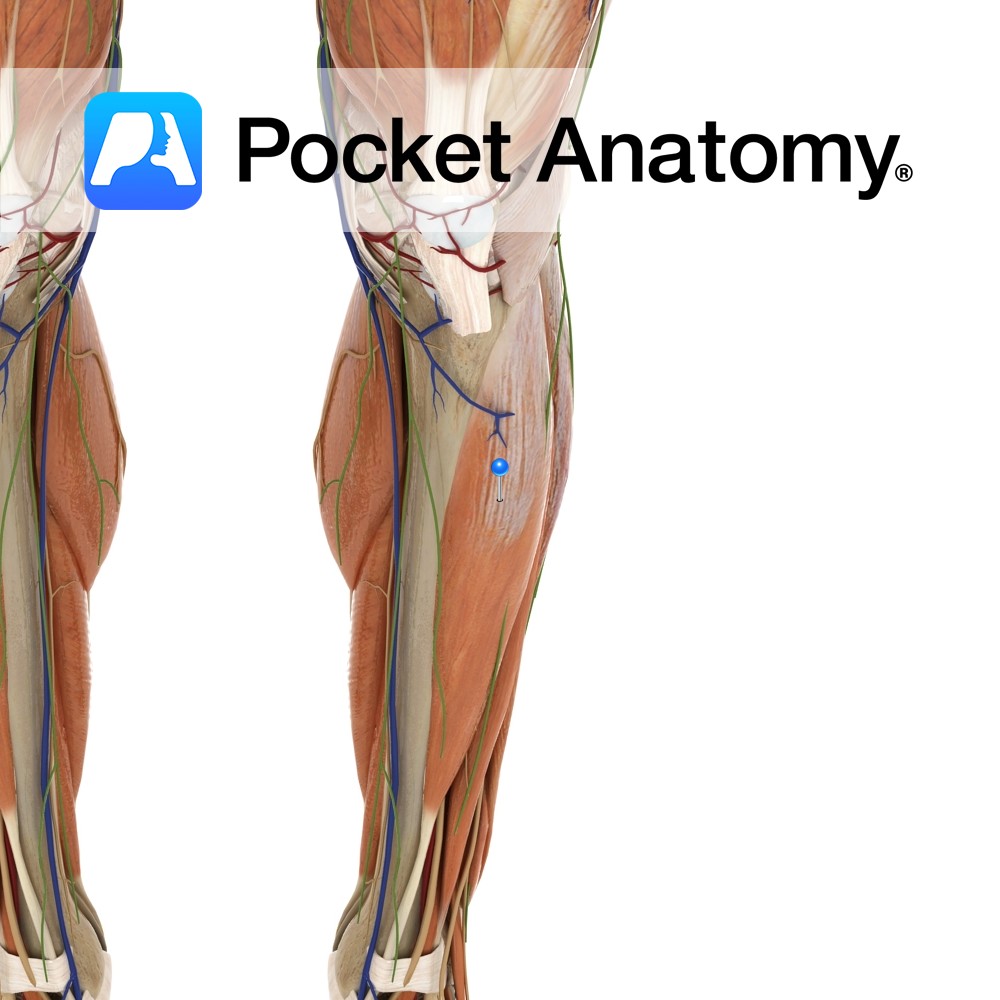
Anatomy
Origin:
Inferior surface of the lateral condyle and upper two-thirds of lateral surface of the tibia and the interosseous membrane.
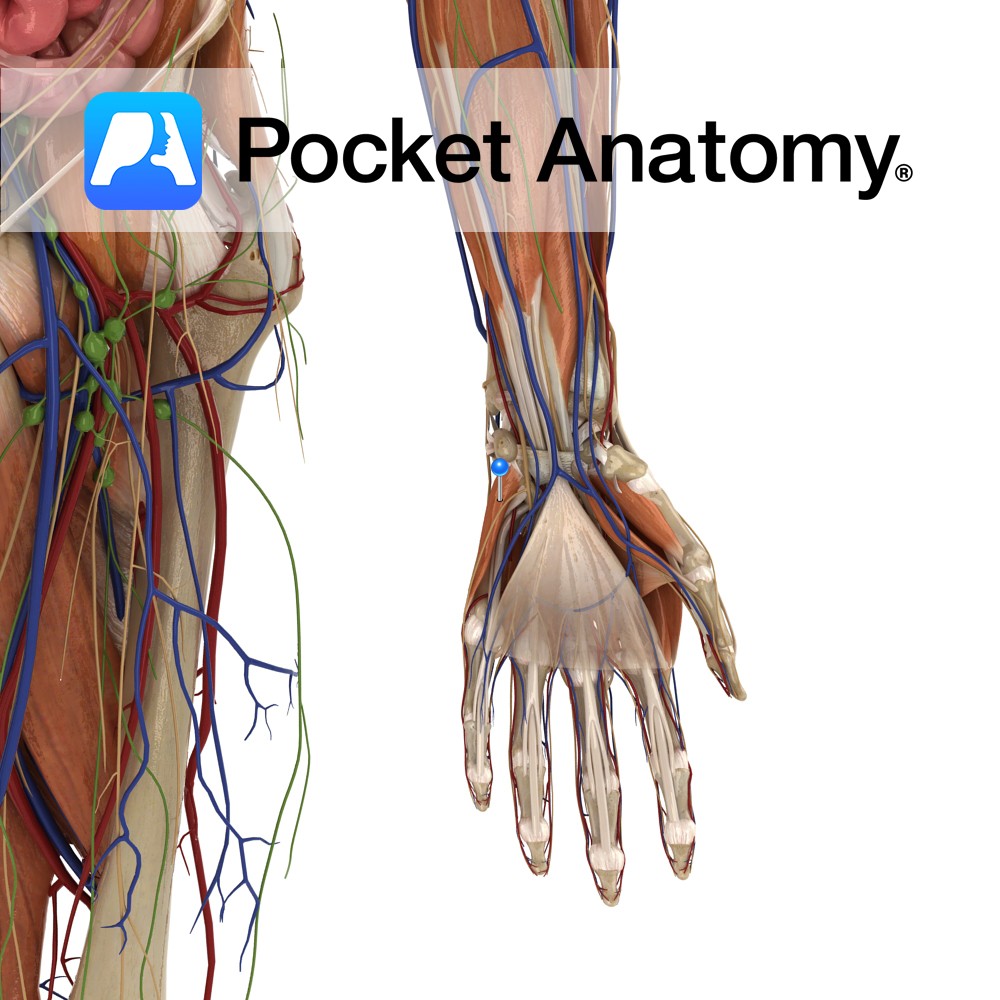
Insertion:
Medial surface of the medial cuneiform and the base of 1st metatarsal.
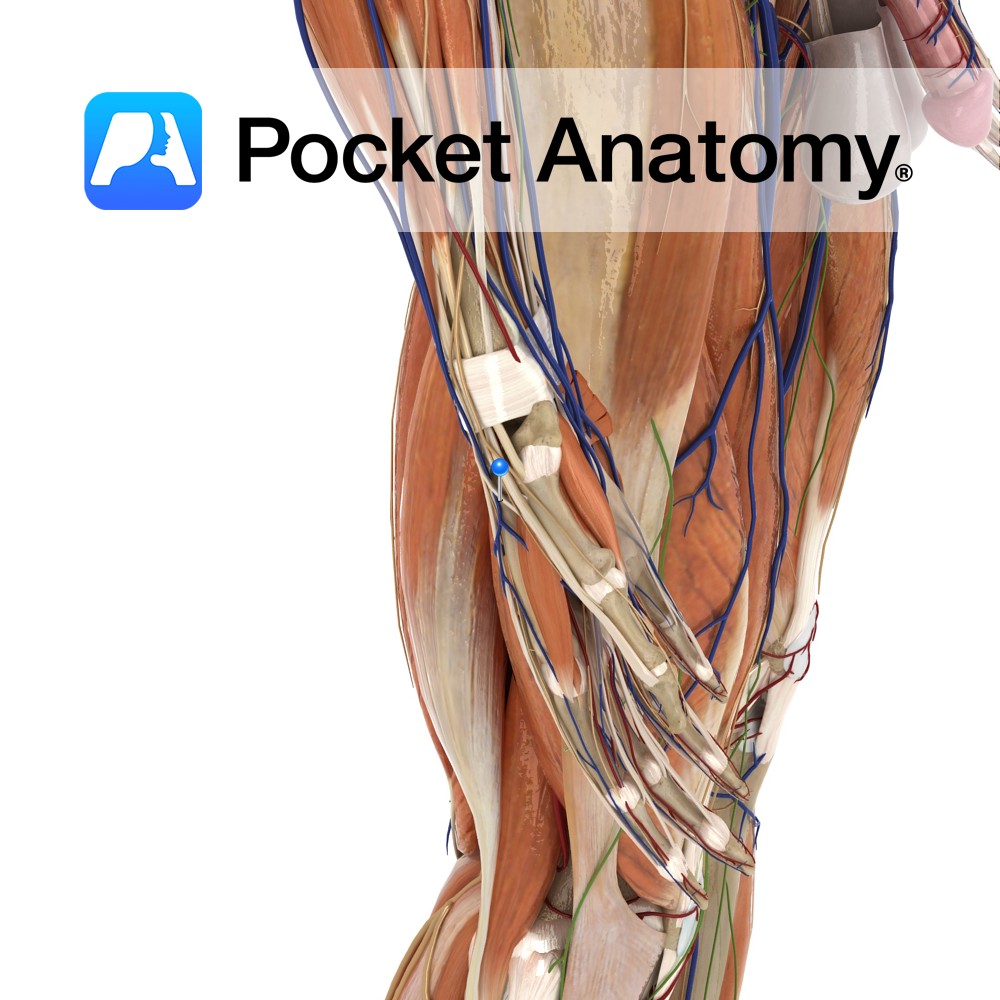
Key Relations:
-One of the four muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg.
-The tibialis anterior tendon crosses anterior to the ankle joint, lateral to the medial malleolus, posterior to the extensor retinaculae.
-The tibialis anterior tendon is visible and palpable through the skin lateral to the anterior border of the tibia.
Functions
-Inverts the foot.
-Dorsiflexes the ankle joint e.g. walking- lifts the foot to clear the ground.
-Supports the medial longitudinal arch of the foot.
Supply
Nerve Supply:
Deep fibular (peroneal) nerve (L4, L5).
Blood Supply:
Anterior tibial artery.
Clinical
Rupture of the tibialis anterior tendon is rare and most commonly affects individuals over the age of fifty. It can occur as a result of ski boots, trauma and is also seen in athletes due to sudden plantarflexion. The patient may present with tenderness, weak dorsifexion, foot drop and ‘slapping’ gait. Treatment may involve surgical repair. Early repair improves the outcome for the patient.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?


.jpg)