PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
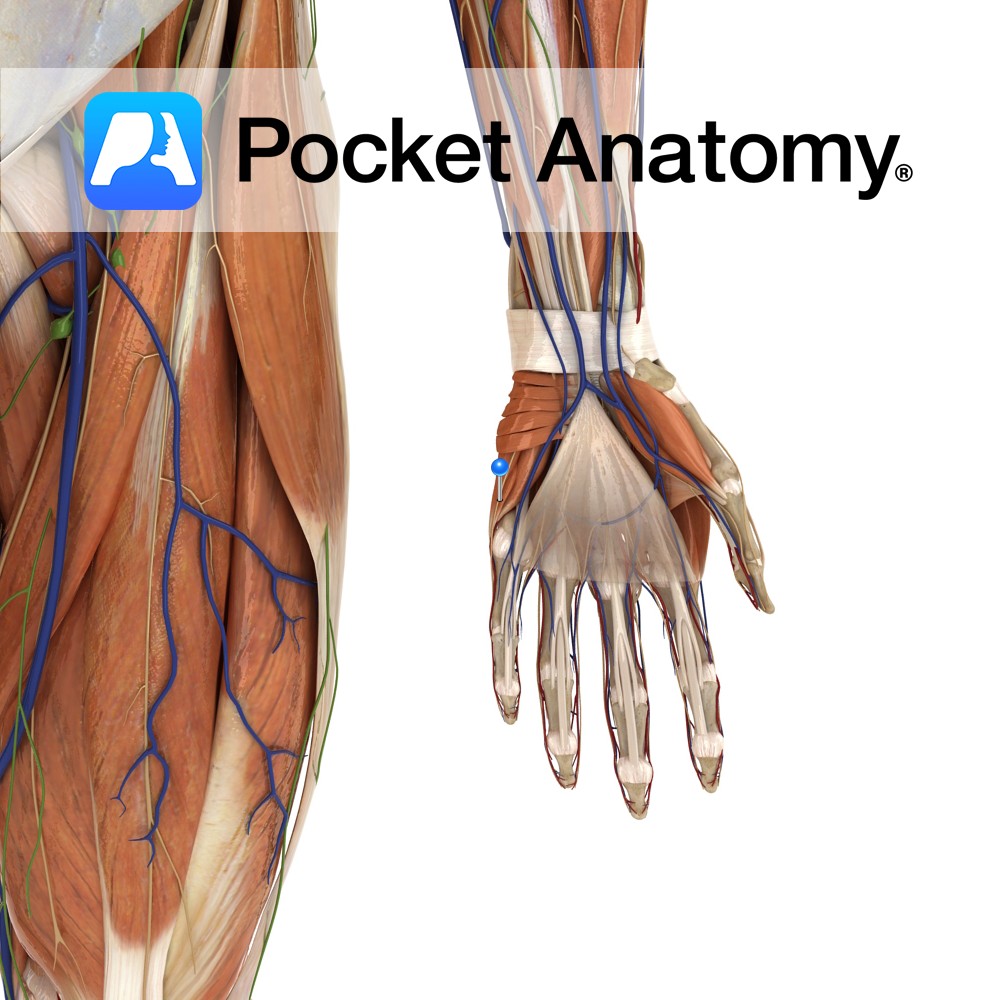
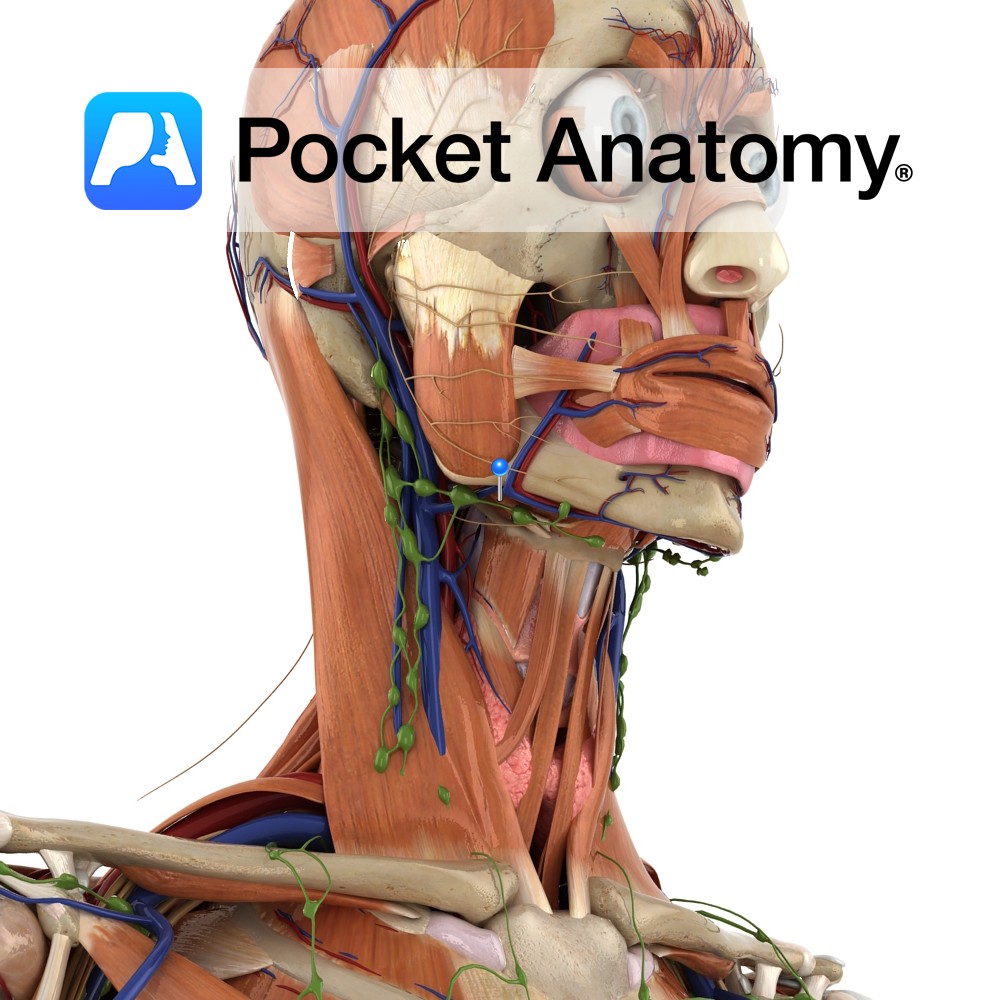
Anatomy Course A terminal branch of the ulnar nerve. Supply Supplies the skin on the medial aspect of the palm with sensory innervation. Clinical Damage may result in pain, a tingling sensation or numbness in its region of distribution. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
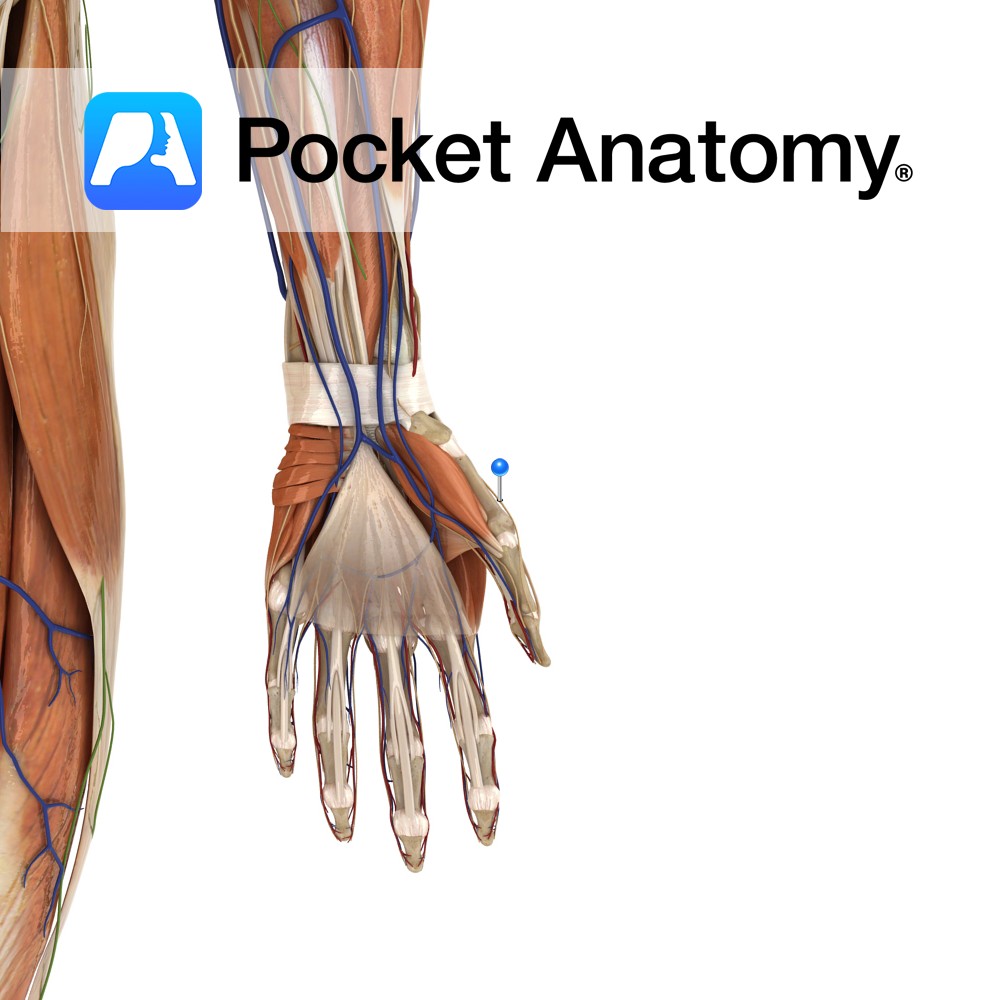
Anatomy Course Branches off from the radial nerve just beyond the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, beneath the brachioradialis muscle. From there it continues to course distally beneath the brachioradialis. Just proximal to the wrist, it emerges from underneath the tendon of the brachioradialis muscle, between it and the tendon of the extensor carpi radialis
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
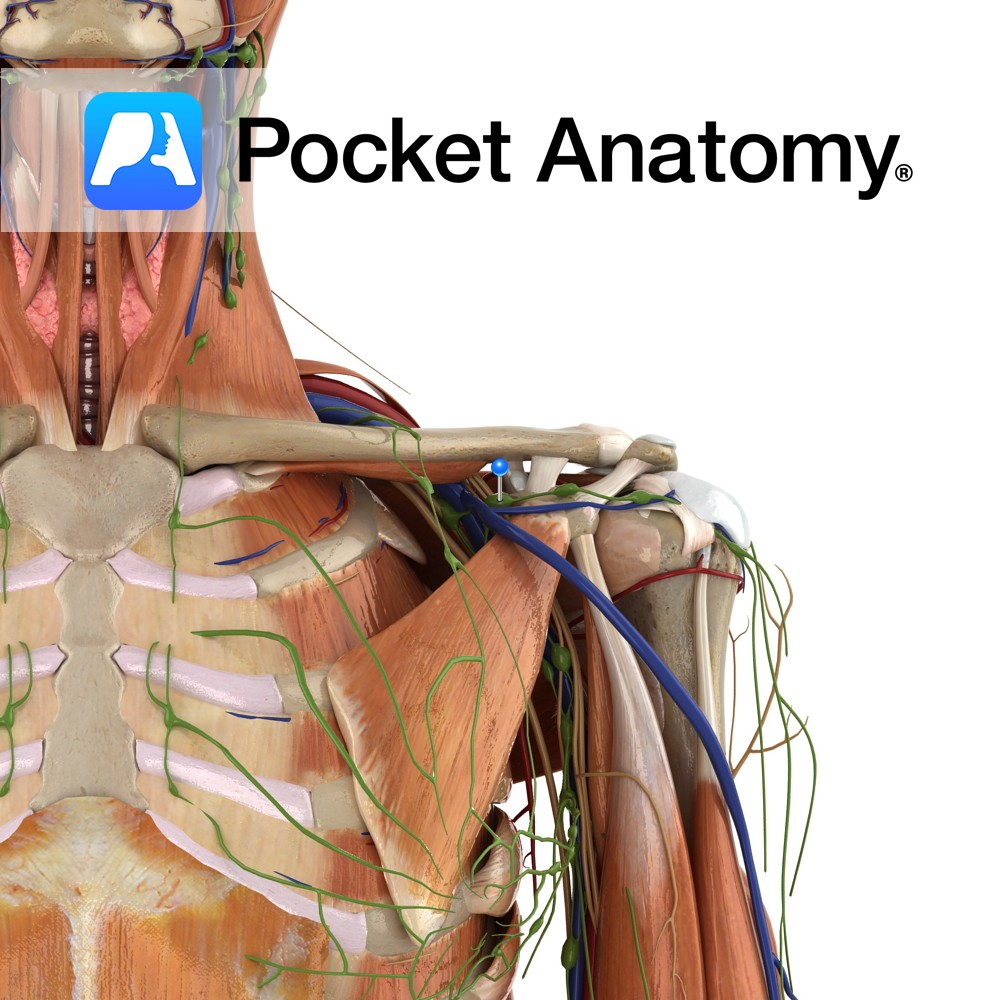
Anatomy Origin: Medial two thirds of the costal surface of the scapula. Insertion: Lesser tubercle of humerus and anterior of capsule of shoulder joint. Key Relations: -Forms much of the posterior axillary wall. -One of the four muscles of the rotator cuff muscle group. Functions -Medially rotates the arm at the glenohumeral joint. -Adducts the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy The subdeltoid bursa lies between the tendon of subscapularis and the fibrous membrane of the glenohumeral joint capsule. Functions The subdeltoid bursa reduces friction between the glenohumeral joint and the tendon of the subscapularis muscle. Clinical Bursitis is swelling of the bursa from infection or overuse. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
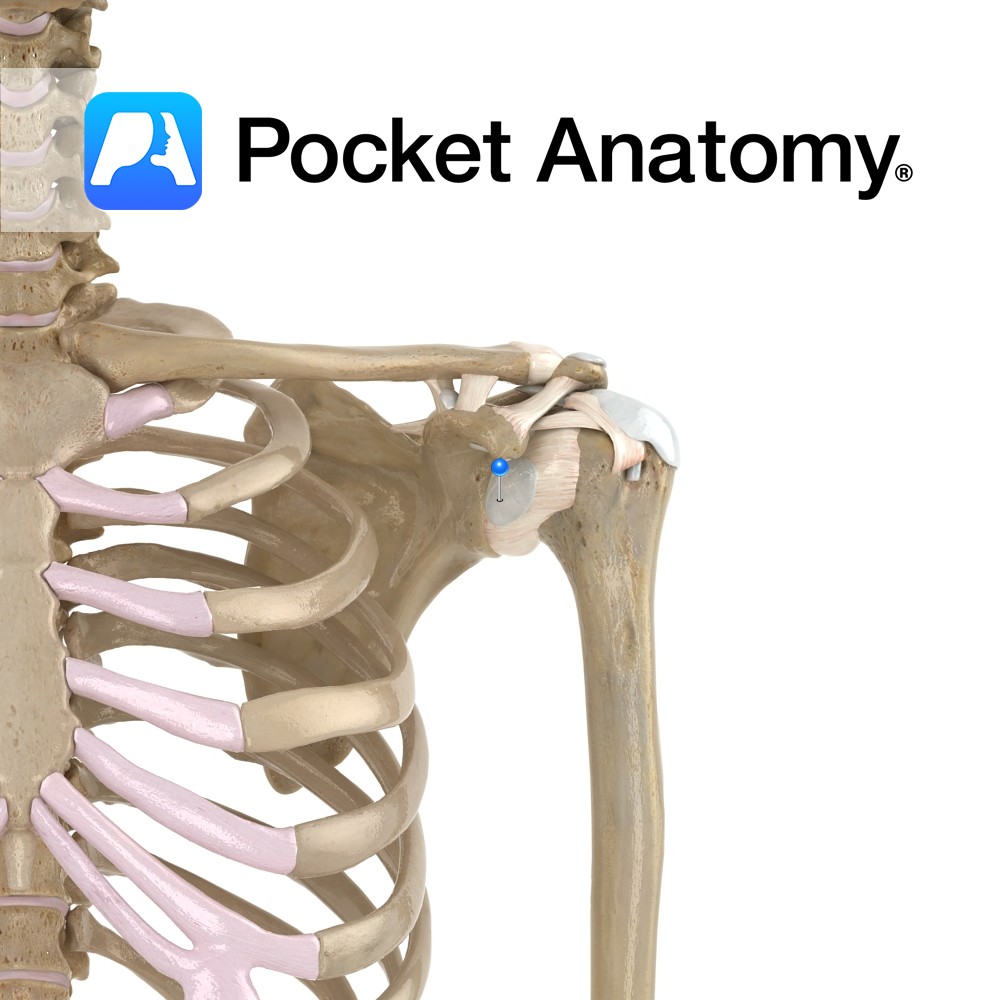
Anatomy Located between the acromion and supraspinatus muscle (or joint capsule). Functions Reduces friction between the acromion and supraspinatus muscle and tendon. Clinical Subdeltoid bursitis is inflammation of the bursa. It is very rare and generally caused by infection or autoimmune inflammation. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
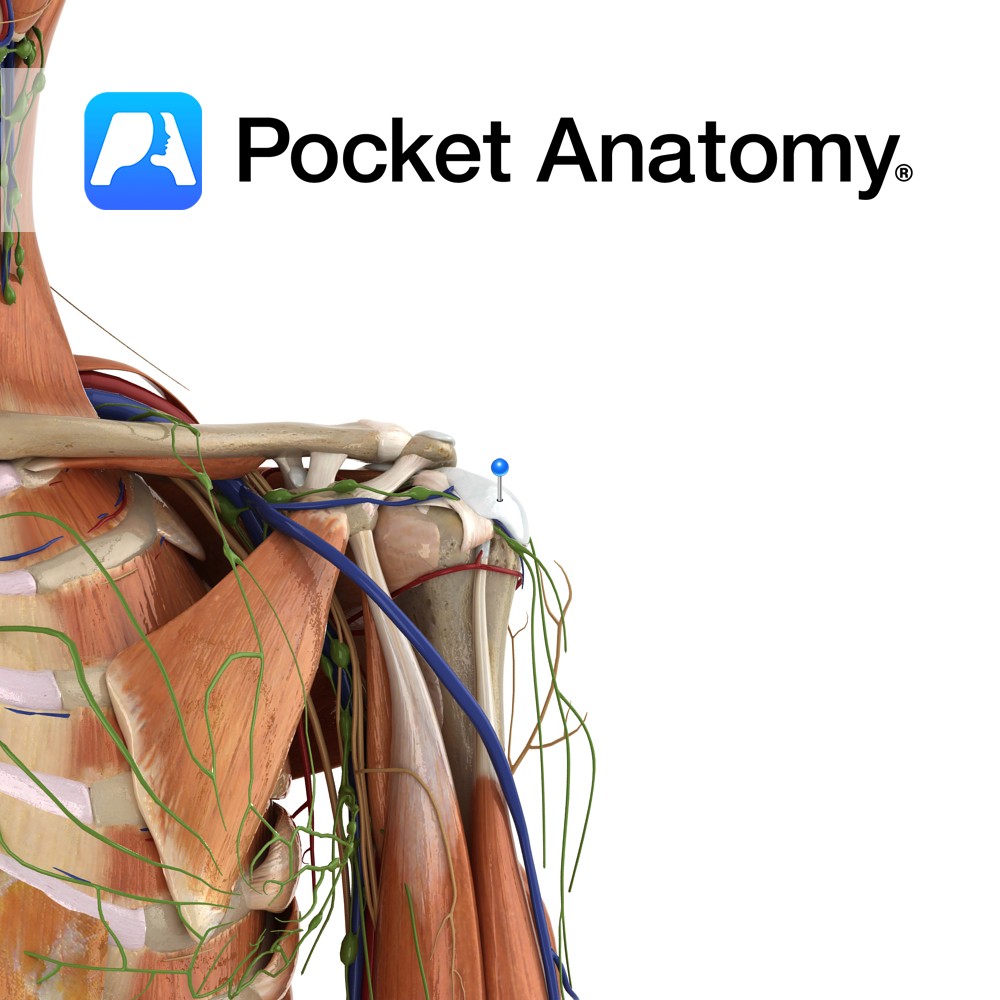
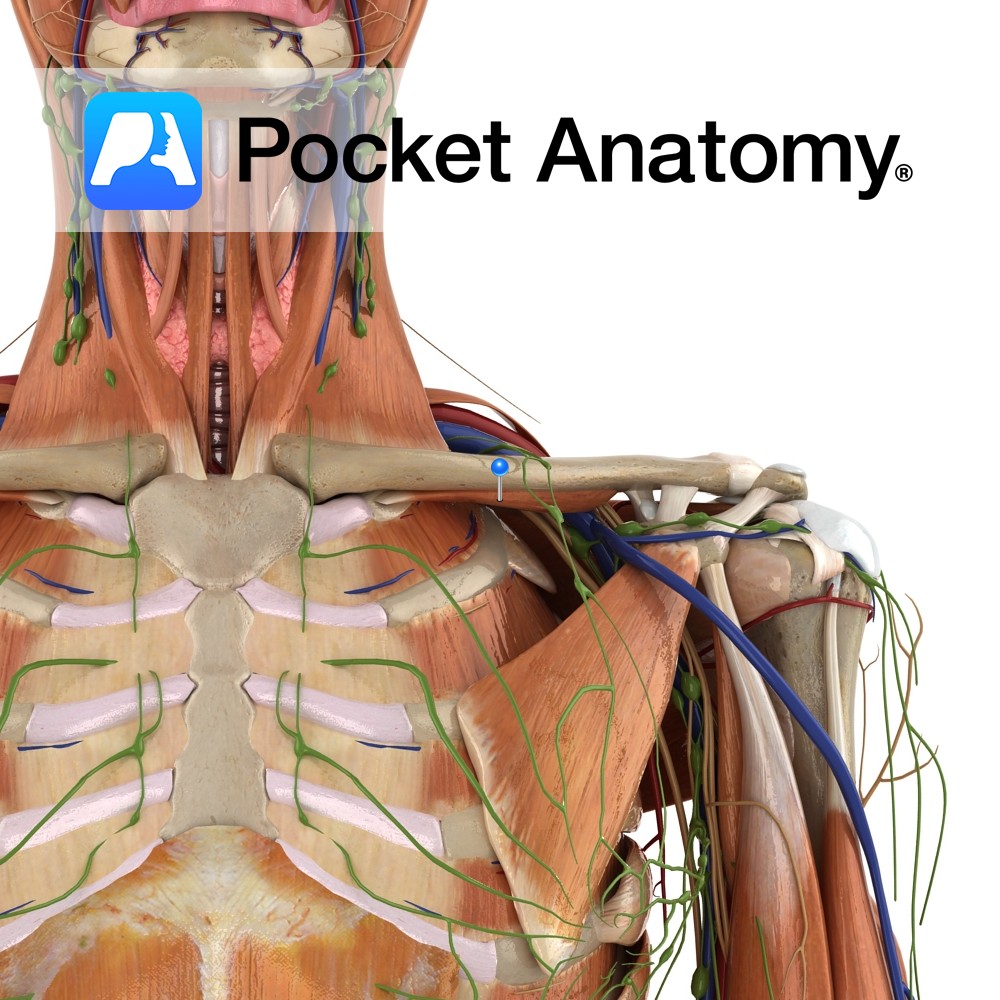
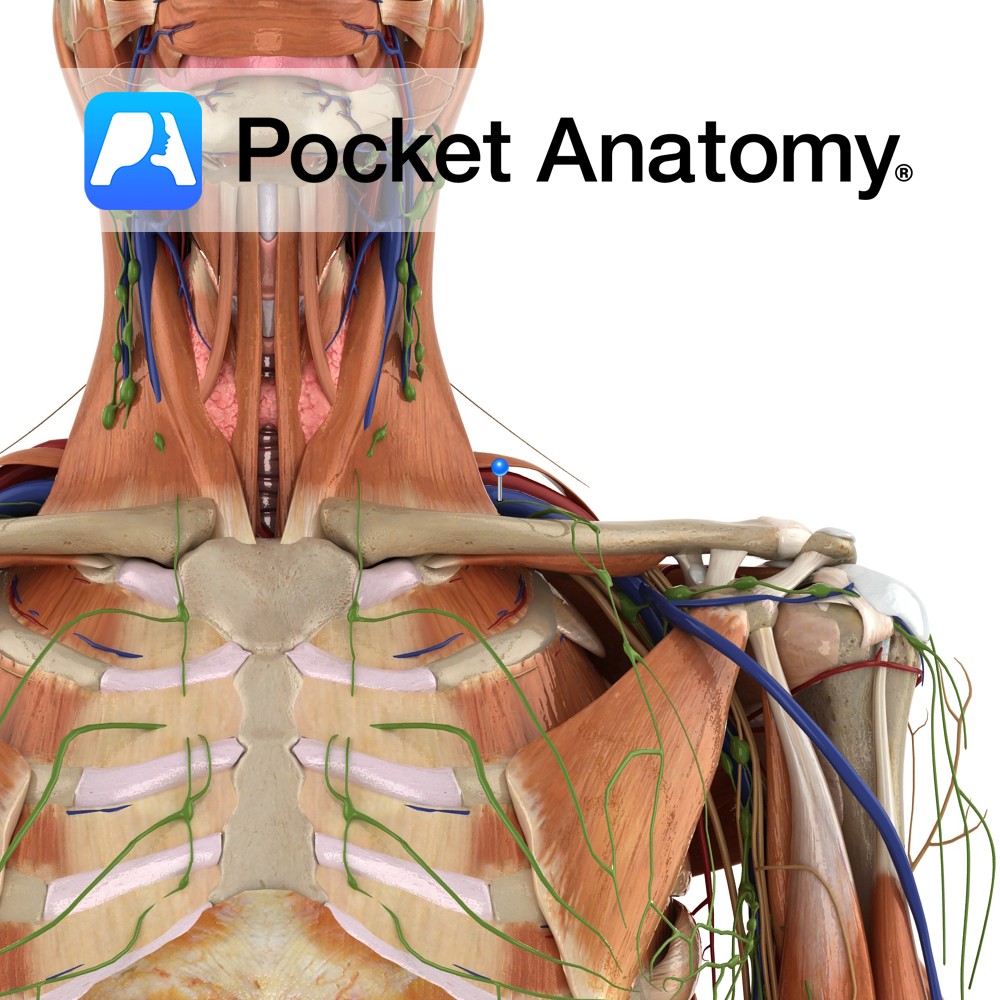
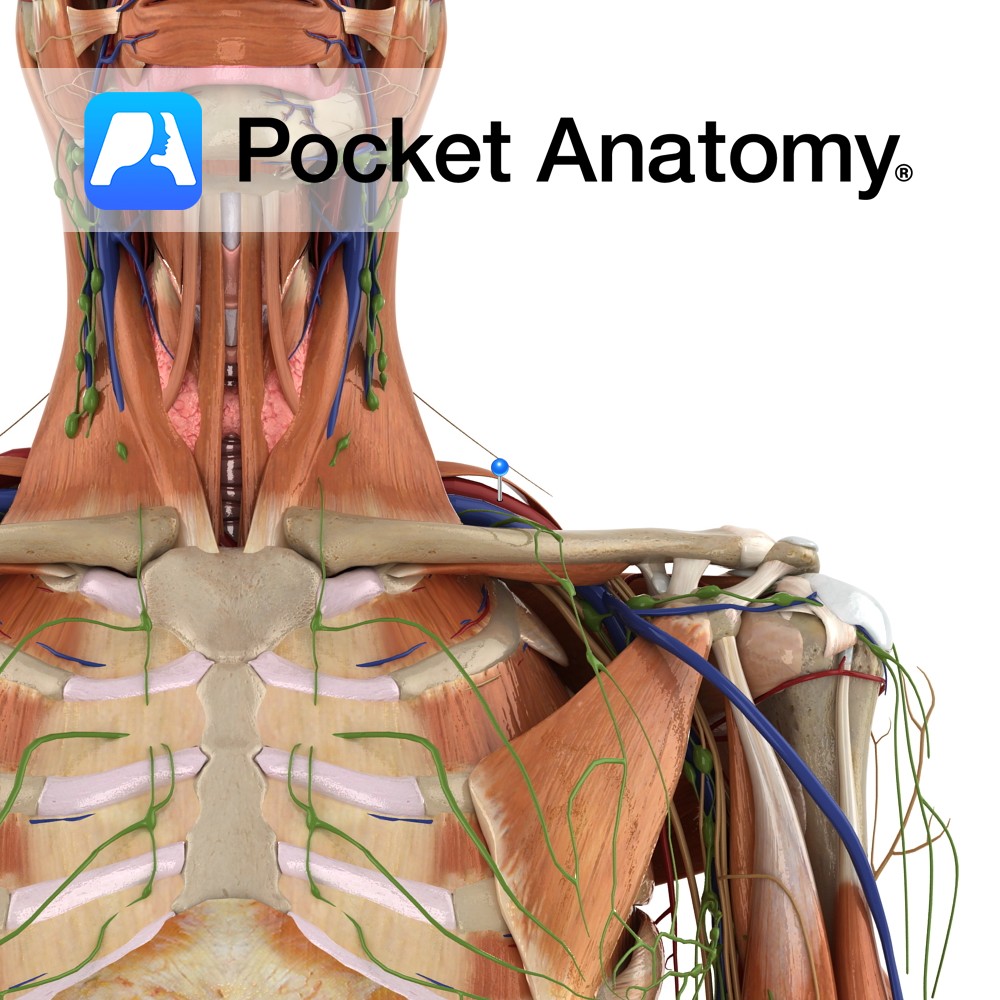
Anatomy Origin: Junction of first rib and costal cartilage. Insertion: Inferior surface of middle third of clavicle in subclavian groove. Key Relations: -Separated posteriorly from the first rib by the subclavian vessels and brachial plexus. -Its insertion is located between the costoclavicular and conoid ligaments. Functions Stabilises the clavicle in the sternoclavicular joint during shoulder
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course A continuation of the axillary vein. It runs along the the margin of the first rib, posterior to the clavicle. It joins with the internal jugular vein at the medial margin of the anterior scalene to form the brachiocephalic vein. Drain Responsible for the venous drainage of the arm and axilla. Interested in
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Course The subclavian arteries are two major vessels in the thorax that pass beneath the clavicles. The left and right subclavian arteries have slightly different courses. The left subclavian artery branches directly from the arch of the aorta, just before it begins its descent. It begins lower in the thorax than the right subclavian
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
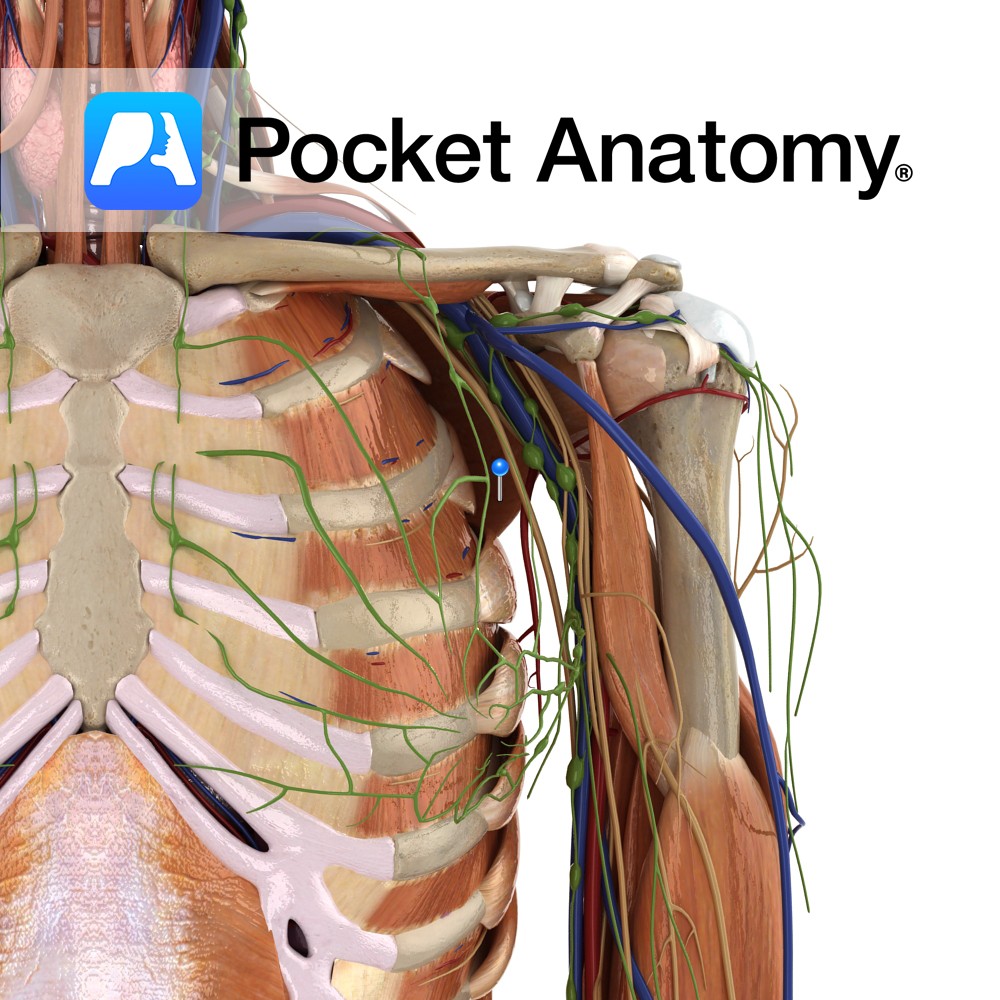
Anatomy One of the 4 paired lymphatic trunks (Jugular, Subclavian, Bronchomediastinal, Lumbar). Subclavian Trunk drains Upper limb, is a triubutary of the Thoracic (or Right Lymphatic) Duct just before it empties into the Subclavain Vein (on L, can be into the L Brachiocephalic Vein). Clinical Lymph and blood capillaries intwerweave basket-like. Lymph Capillaries have no
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Base of styloid process of the temporal bone. Insertion: Base of greater cornu of hyoid bone. Key Relations: -Is one of the suprahyoid muscles lying in the anterior triangle of the neck. -Perforated near it’s insertion by the intermediate tendon of the digastric muscle. -Anteromedial to stylohyoid is another suprahyoid muscle geniohyoid. Functions
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins