PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
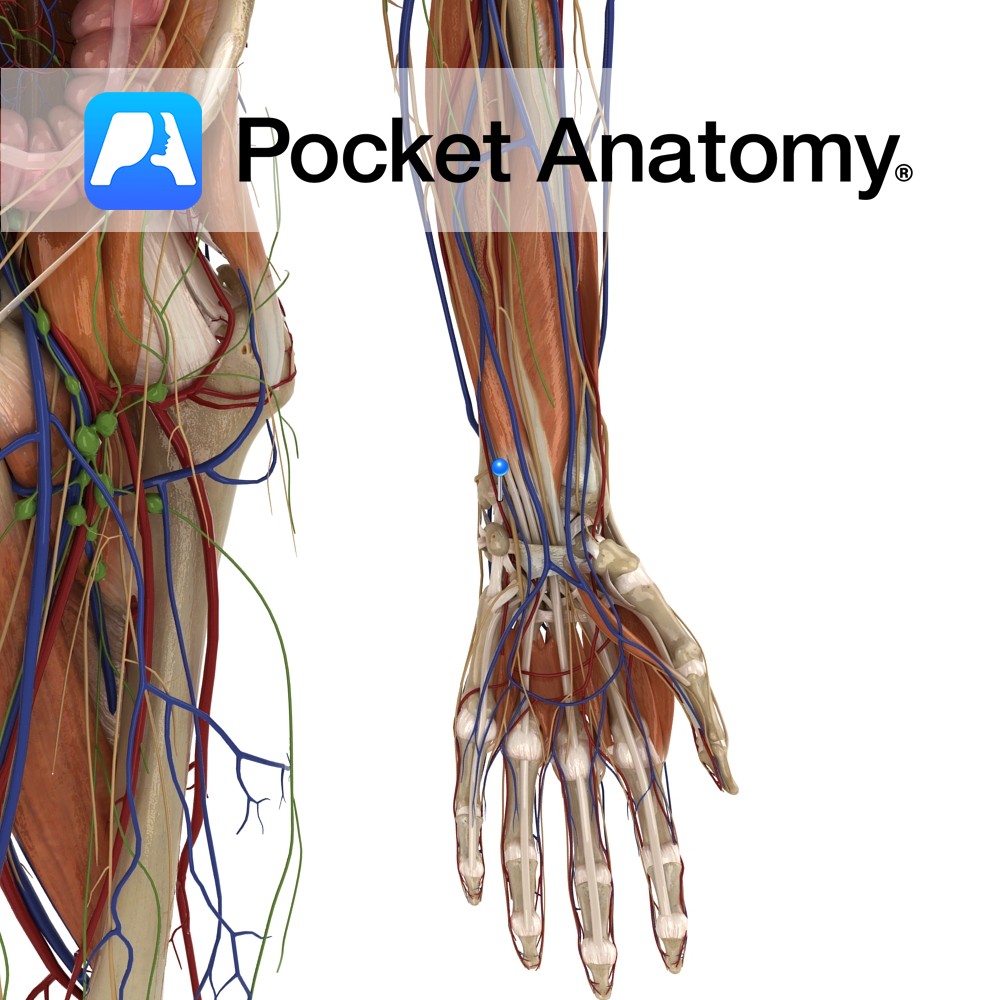
Anatomy Course A branch of the brachial artery. It travels along the medial side of the arm. It runs deep in the arm, running along the flexor digitorum profundus muscle for the most of its course. It becomes most medial about halfway down the ulna. It enters the hand just lateral to the pisiform bone,
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
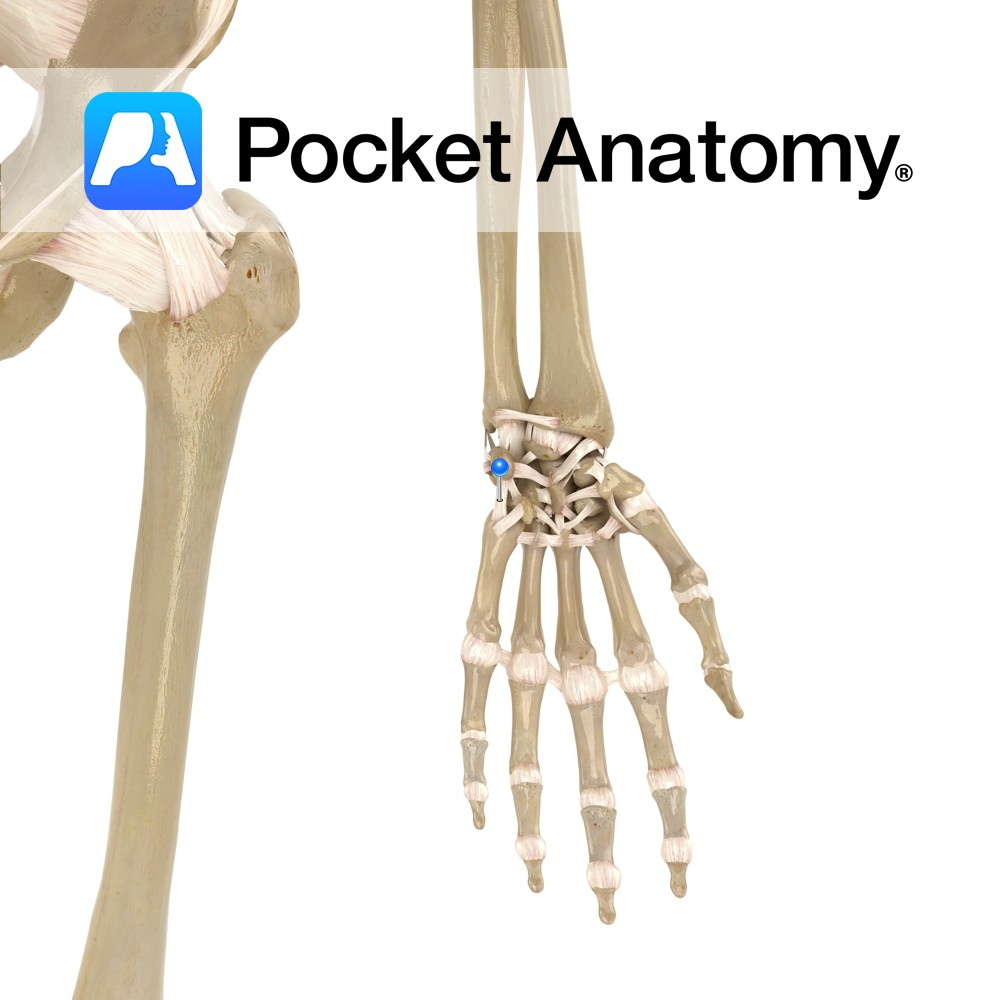
Anatomy Attaches from the palmar surface of the ulna, passing to the medial surfaces of the triquetrum with slips to hamate bone. Functions Provides static stability to the wrist and carpal joints. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: The trigeminal motor nucleus is located in the mid pons tegmentum and the trigeminal sensory nucleus extends the length of the brain stem and upper cervical cord. Its subnuclei include the principal sensory nucleus located in the pontine tegmentum, the mesencephalic nucleus extending into the midbrain and the spinal nucleus extending through the
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Small finger side of nearer row of carpal bones, pyramidal shape. Articulates out with lunate, down with hamate, in front (palmar) with pisiform. On ulnar side but does not articulate with it. Clinical The palmar (anterior) aspect of the carpus is concave and, covered with the flexor retinaculum (ligament), forms the carpal tunnel. Interested
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
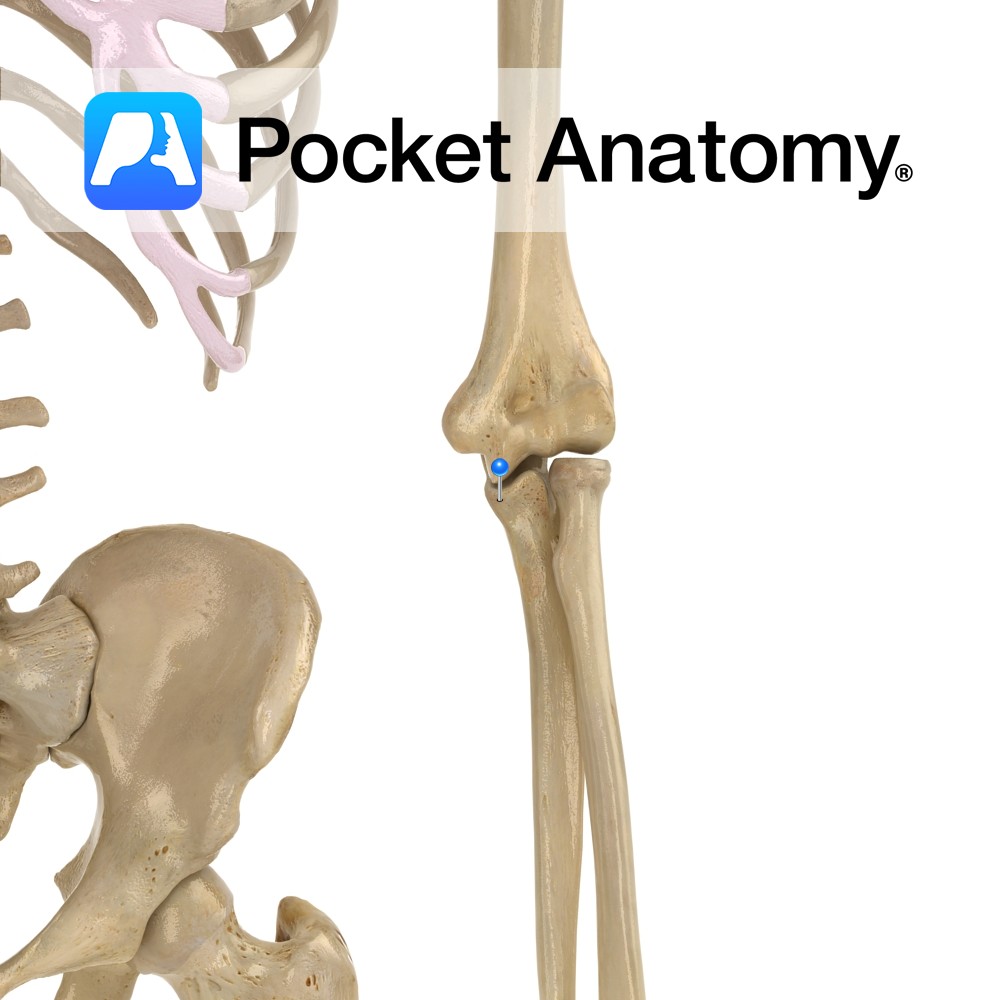
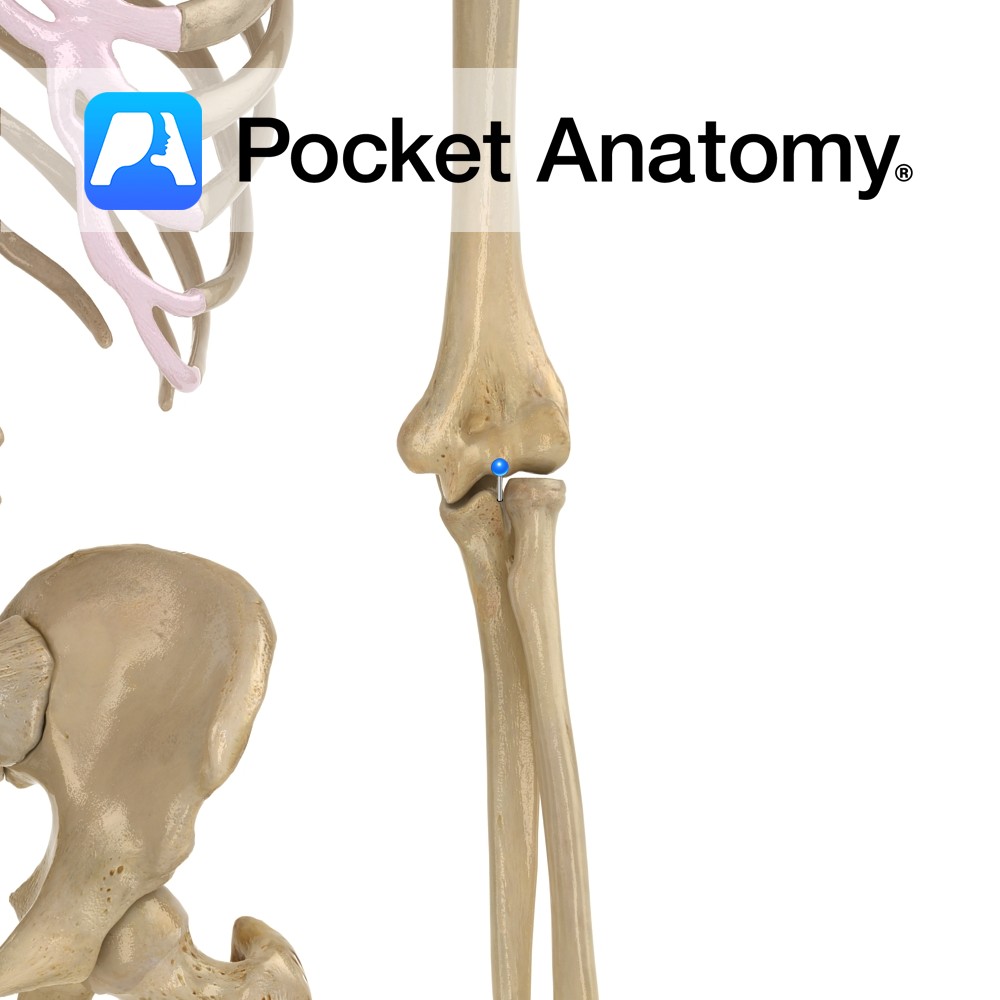
Anatomy Separated from olecranon by trochlear notch, sits in coronoid fossa of humerus, just above trochlea, when elbow bent (elbow flexed). The radial notch is at its lateral edge. Attachments; brachialis, parts of flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus, pronator teres, sometimes flexor pollicis longus. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
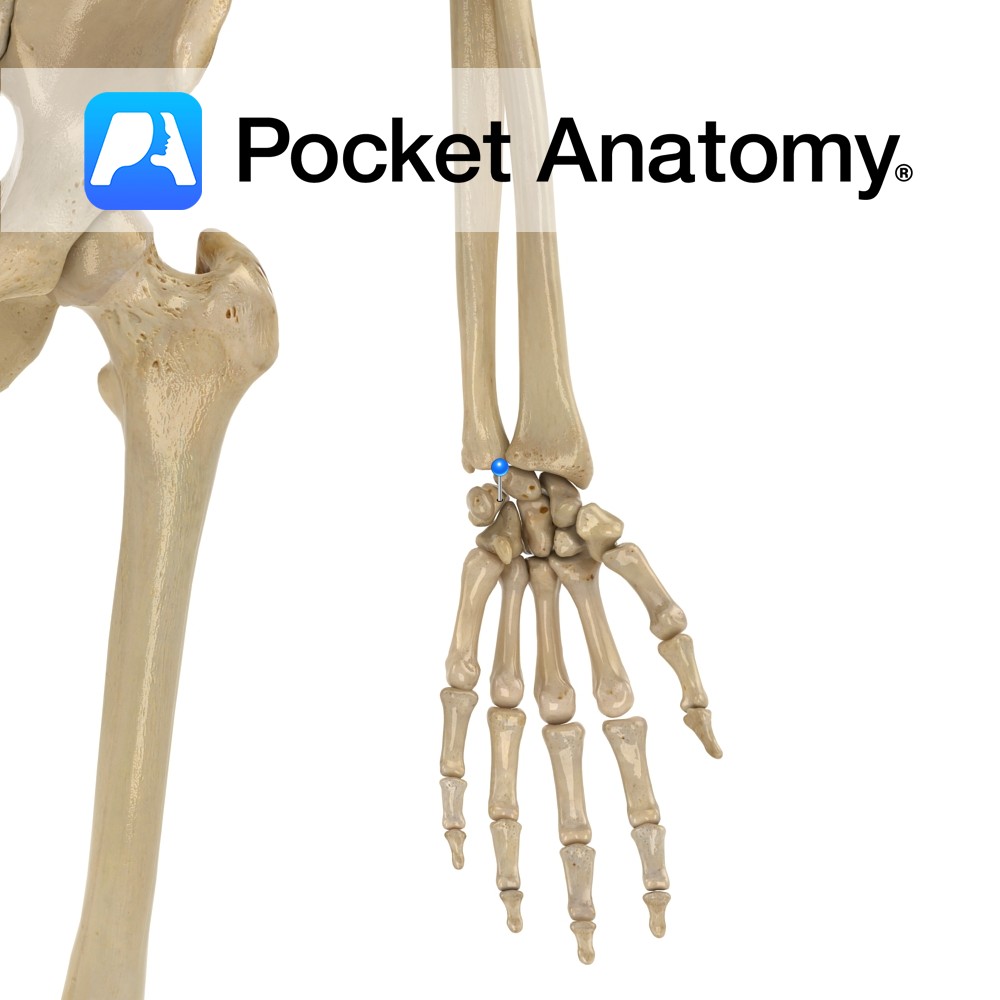
Anatomy Articulates down with articular disc between it and wrist joint, and laterally with the ulnar notch of the radius (pivot joint). Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
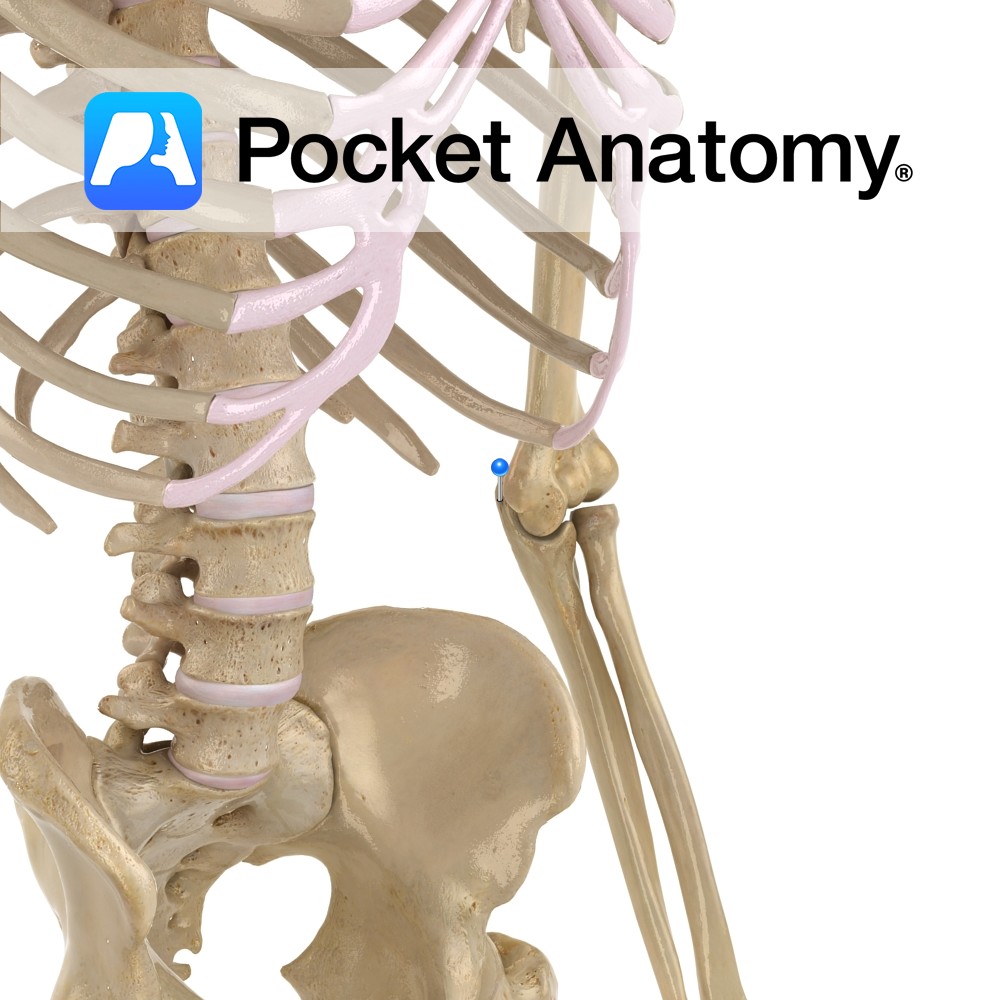
Anatomy Curved bulge upper end ulna, sits, when elbow extended, in olecranon fossa at back of bottom of humerus, lending significant bony strength, stability and movement limitation (stopping hyperextension). Attachments; triceps brachii, posterior and ulnar collateral ligaments. Clinical Back of olecranon process covered by bursa, just subcutaneous; bursitis in trauma, infection, pressure, rheumatoid arthritis, gout.
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
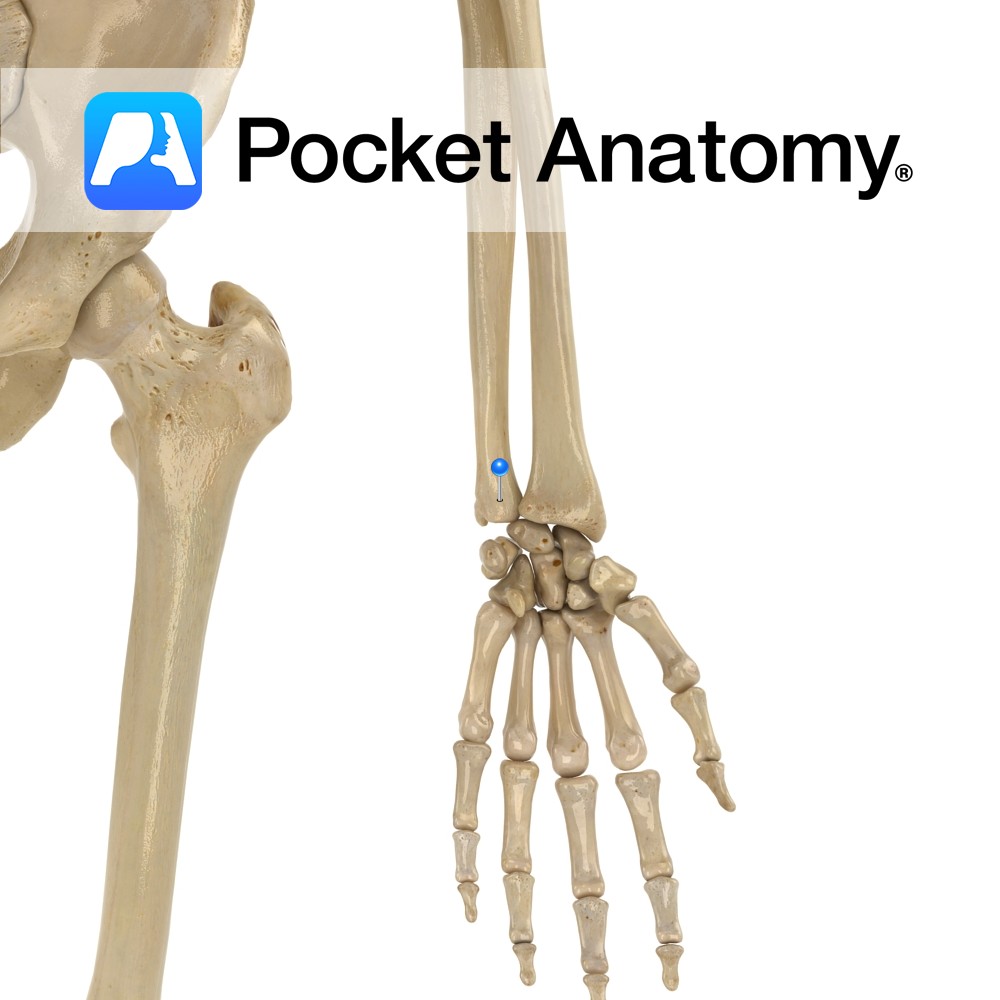
Anatomy The radial head articulates with (rolls over) the radial notch of ulna, manifest as pronation and supination. At the lower end of the forearm, the ulnar head articulates with the ulnar notch of the radial head. Clinical Radial head is proximal and articulates with a notch on the ulna; ulnar head is distal and
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
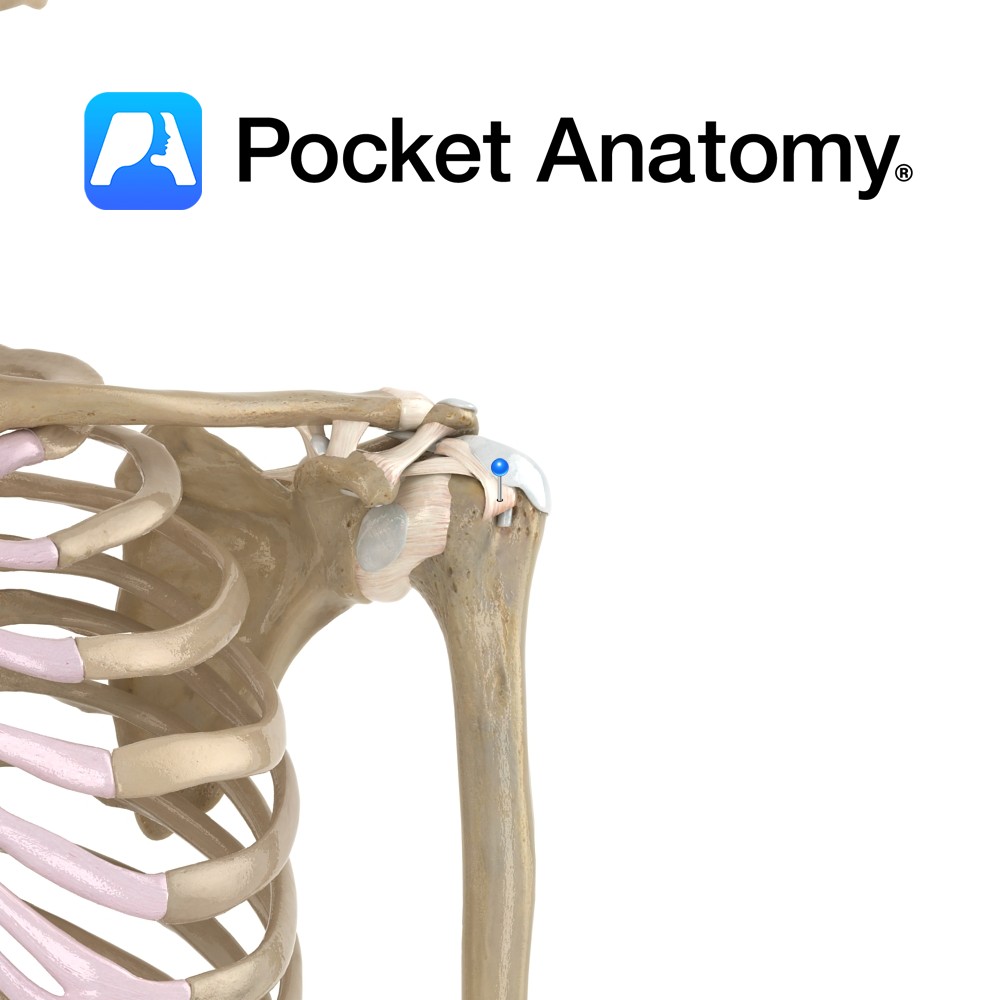
Anatomy A thin band attaching across the proximal part of the bicipital groove. Functions Holds the tendon of the log head of biceps brachii in place as it passes up towards its origin. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
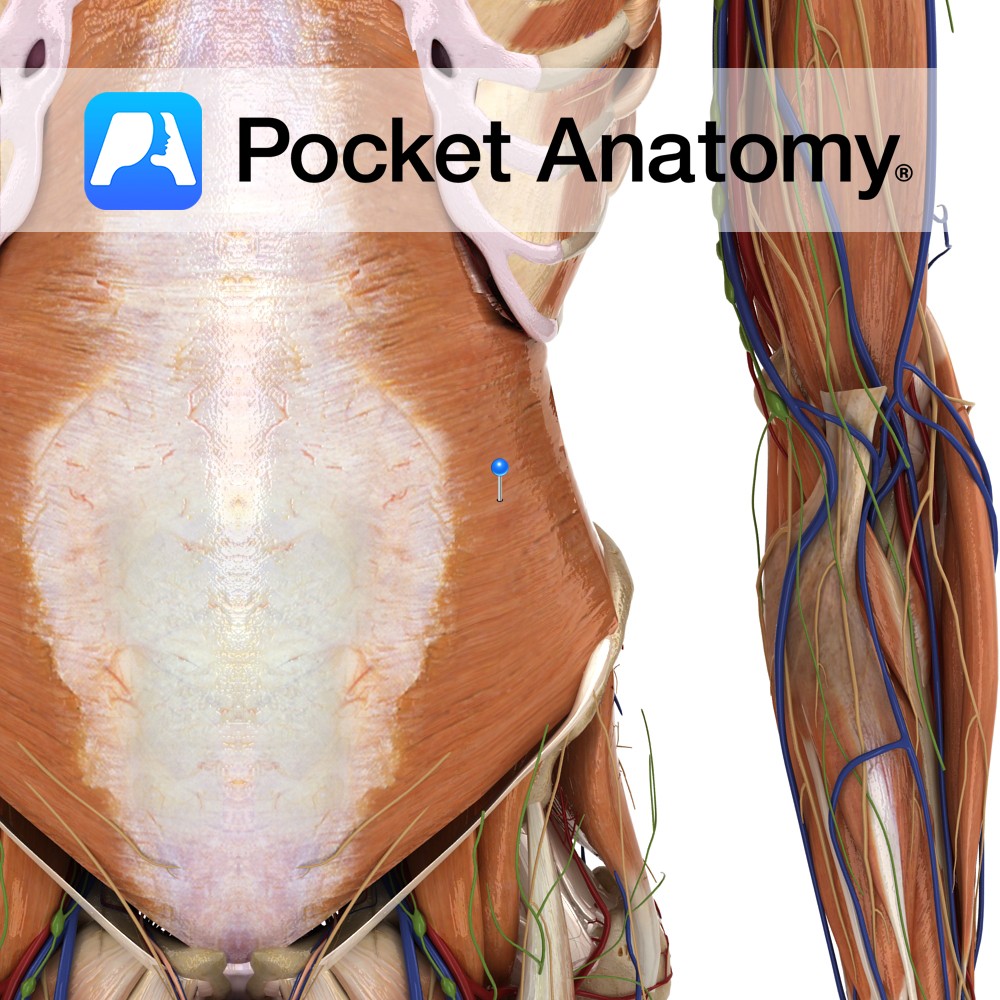
Anatomy Origin: Thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest, inguinal ligament, costal cartilages and 7th to 12th ribs. Insertion: Xiphoid process, aponeruosis ending in linea alba, pubic crest and pectineal line. Key relations: -Deep to the internal obliques. -Muscle fibres run transversely as the name suggests. -Superior three-quarters lies posterior to the rectus abdominis. -Inferior quarter lies anterior
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)