Anatomy
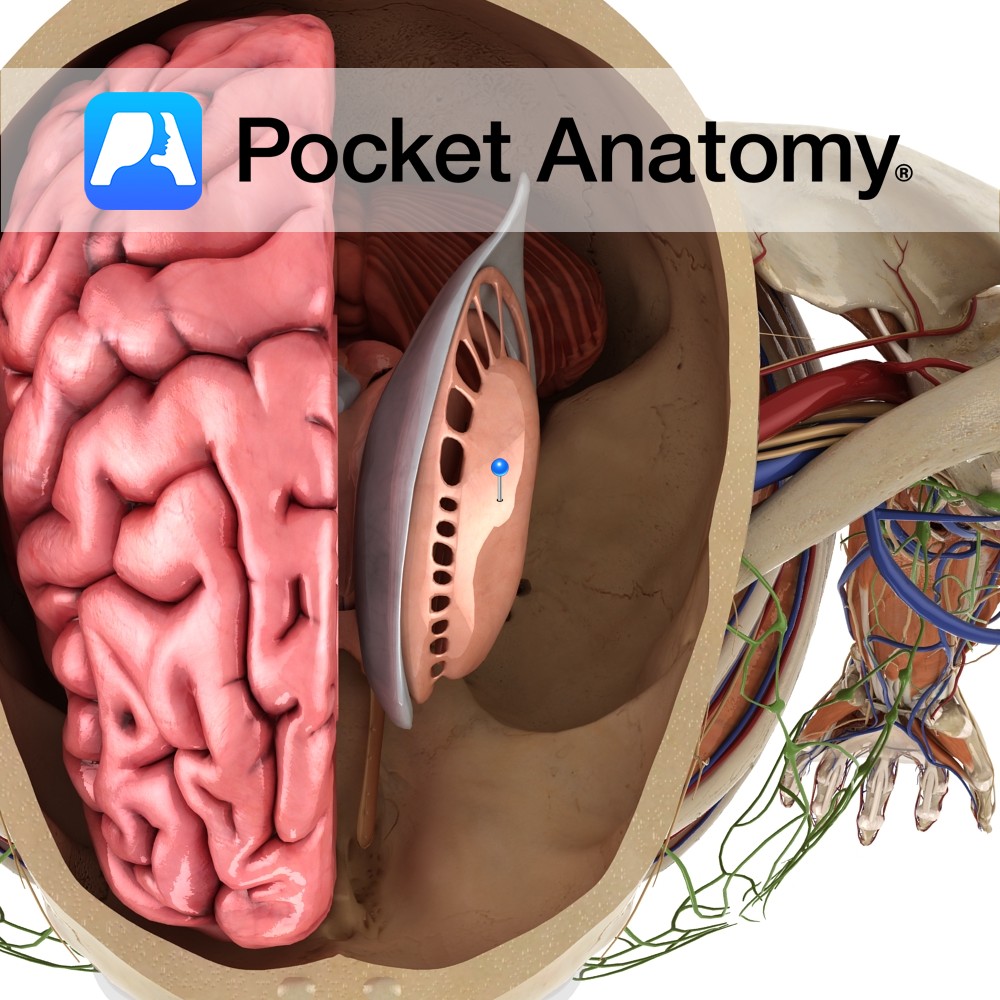
The basal ganglia is a collection of nuclear masses located within each cerebral hemisphere. The most prominent bodies are the caudate nucleus, putamen and globus pallidus. These nuclei are collectively referred to as the corpus striatum.
Blood Supply:
Supplied by branches of the internal carotid, anterior cerebral and middle cerebral arteries.
Functions
The basal ganglia, in association with the subthalamic nucleus and ventral thalamus, regulates the activity of upper motor neurons and modulates movement.
The basal ganglia has also been implicated in learning and memory. It may play a role in deciding which action from a group of actions is the most suitable for execution.
Clinical
Disorders of the basal ganglion may give rise to movement disorders which may be broadly classified as hyperkinetic (chorea, myoclonus, dystonia, temor, athetosis, ballismus) or hypokinetic (parkinsonism). Importantly, some of these mentioned hyperkinetic movement disorders may also be a prominent feature of conditions where the main pathology lies outside the basal ganglia i.e. myoclonus, dystonia, tremor, are not specific to the basal ganglia). Parkinsonism is characterised by the cardinal features of bradykinesia, rigidity, resting tremor, stooped posture, falls.
Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease (PD) arises from a deficiency of dopamine in the caudate and putamen, caused by the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the pars compacta of the substantia nigra. This damage reduces the activity of the Direct Pathway and increases the activity of the Indirect Pathway, ultimately impairing movement.
Huntington’s Disease (HD) arises from the accumulation of the mutant protein ‘Huntingtin’, causing degeneration in the caudate and putamen. This damage increases the activity of the Direct Pathway and decreases the activity of the Indirect Pathway, ultimately increasing movement. Huntington’s disease results in chorea, psychiatric changes, and progressive cognitive impairment.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?


.jpg)