Anatomy
Origin:
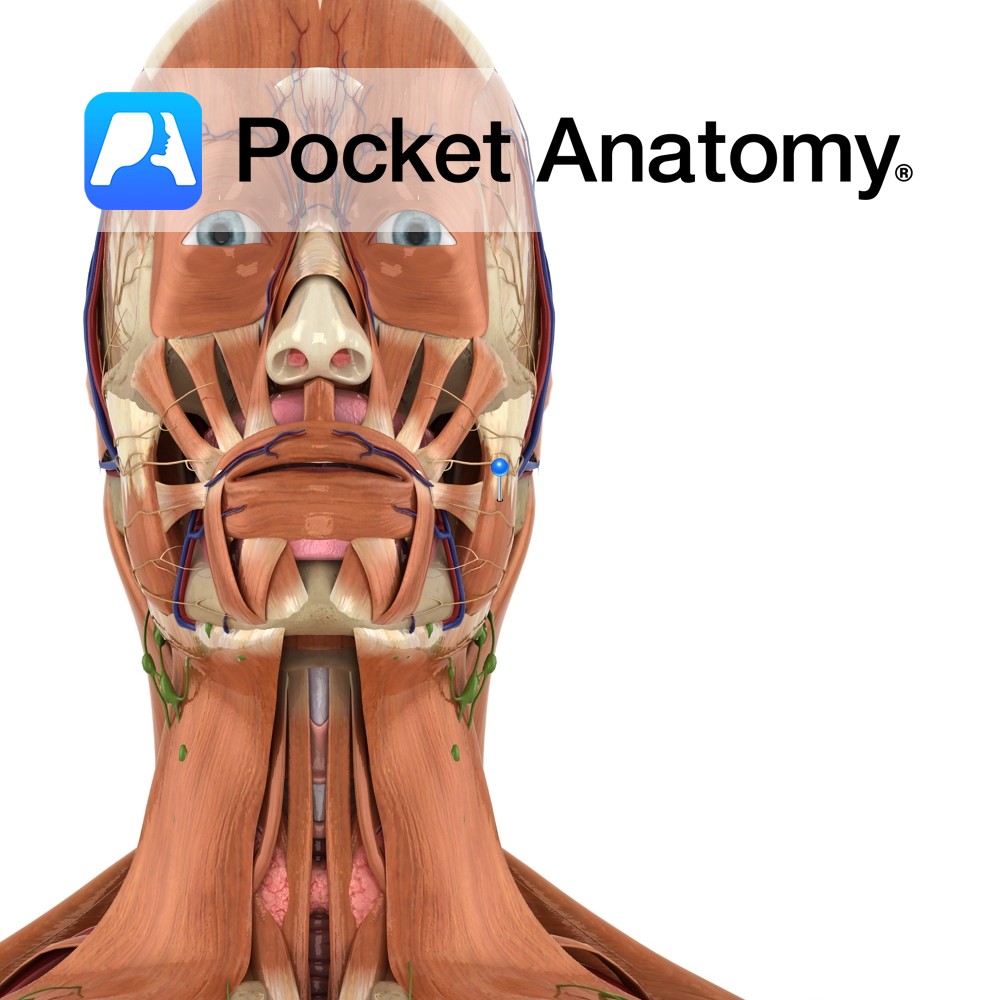
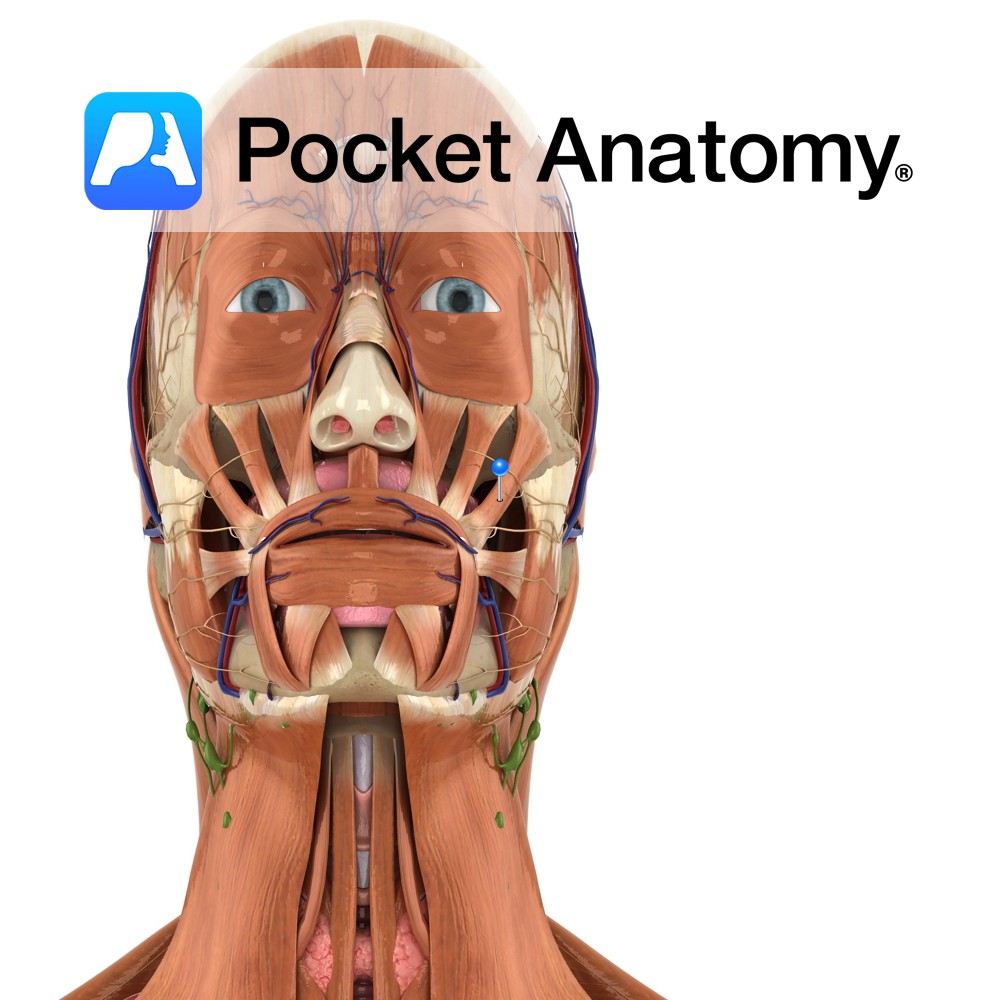
Superficial and Deep portion: Inferior border and medial surface of zygomatic arch.
Insertion:
Superficial and Deep portion: Outer aspect of angle of jaw and lower half of ramus of mandible.
Key Relations:
-The superficial portion is larger and thicker whereas the deep portion is much smaller.
-The muscle is crossed superficially by the parotid duct, branches of the facial nerve and the transverse facial vessels.
-One of the four muscles of mastication.
Functions
Elevates the mandible to occlude the teeth in mastication.
e.g. as in closing the mouth..
Supply
Nerve Supply:
Mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN 5).
Blood Supply:
-Masseteric branch of the maxillary artery
-Transverse facial branch of superficial temporal artery
–Facial artery.
Clinical
Testing the bulk and power of the temporalis and masseter muscles can be useful in the detection of a CN 5 lesion. Muscle bulk can be palpated above the mandible. Power can be tested by asking the patient to bite forcefully onto a wooden tongue depressor and trying to remove it from their mouth. A bite of normal strength will prevent this.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?