Anatomy
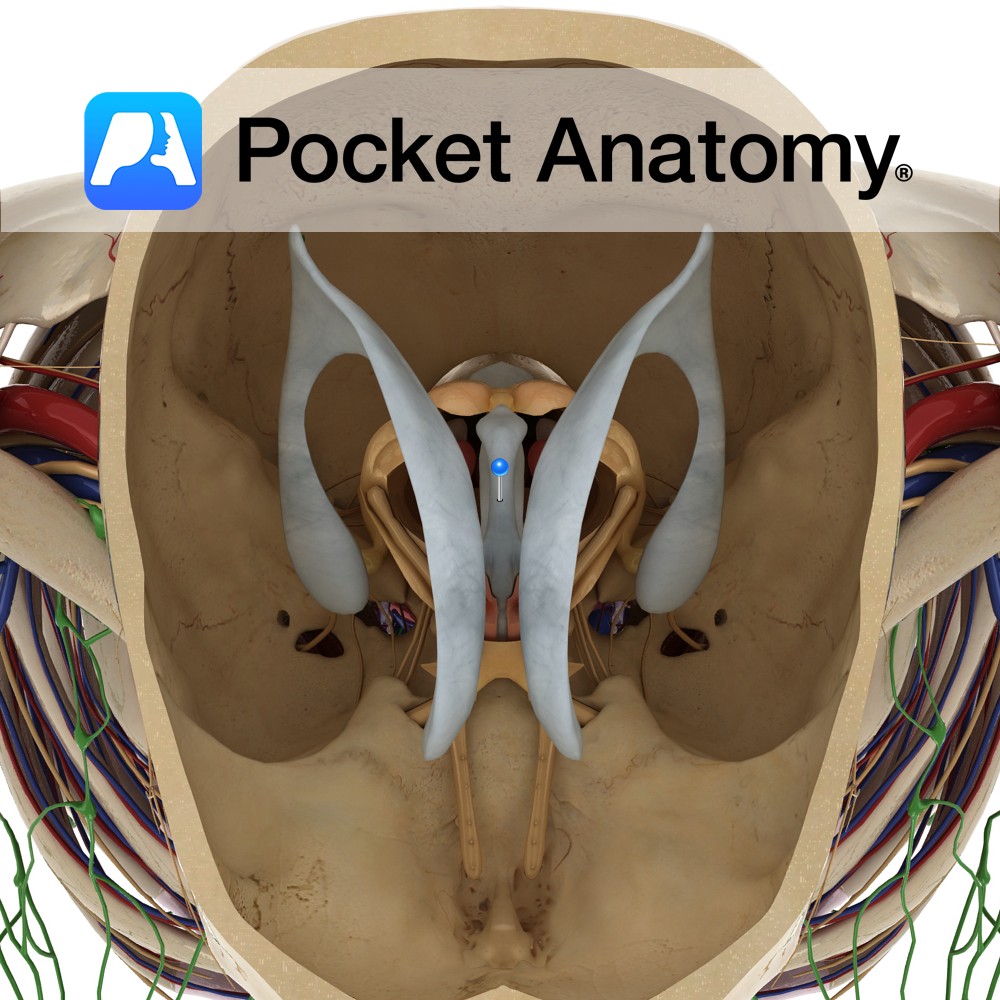
Is a slit-like cavity lined with ependymal cells, located between the two thalami and is a part of the series of fluid-filled cavities, which make up the ventricular system. It is connected anteriorly to the lateral ventricles via the interventricular foramen of Monro.
The anterior wall is formed by the lamina terminalis. The lateral wall is formed by the medial surface of the thalamus and hypothalamus. The posterior wall opens into the cerebral aqueduct of Sylvius connecting the third ventricle with the fourth ventricle.
Functions
Filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and drains CSF from the lateral ventricles to the fourth ventricle.
Clinical
Obstructive hydrocephalus may occur when there is a blockage to CSF flow through the third ventricle. This can lead to dilatation of the ventricles with resultant damage to brain tissue.
Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?