PocketAnatomy® is a registered brand name owned by © eMedia Interactive Ltd, 2009-2022.
iPhone, iPad, iPad Pro and Mac are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries. App Store is a service mark of Apple Inc.
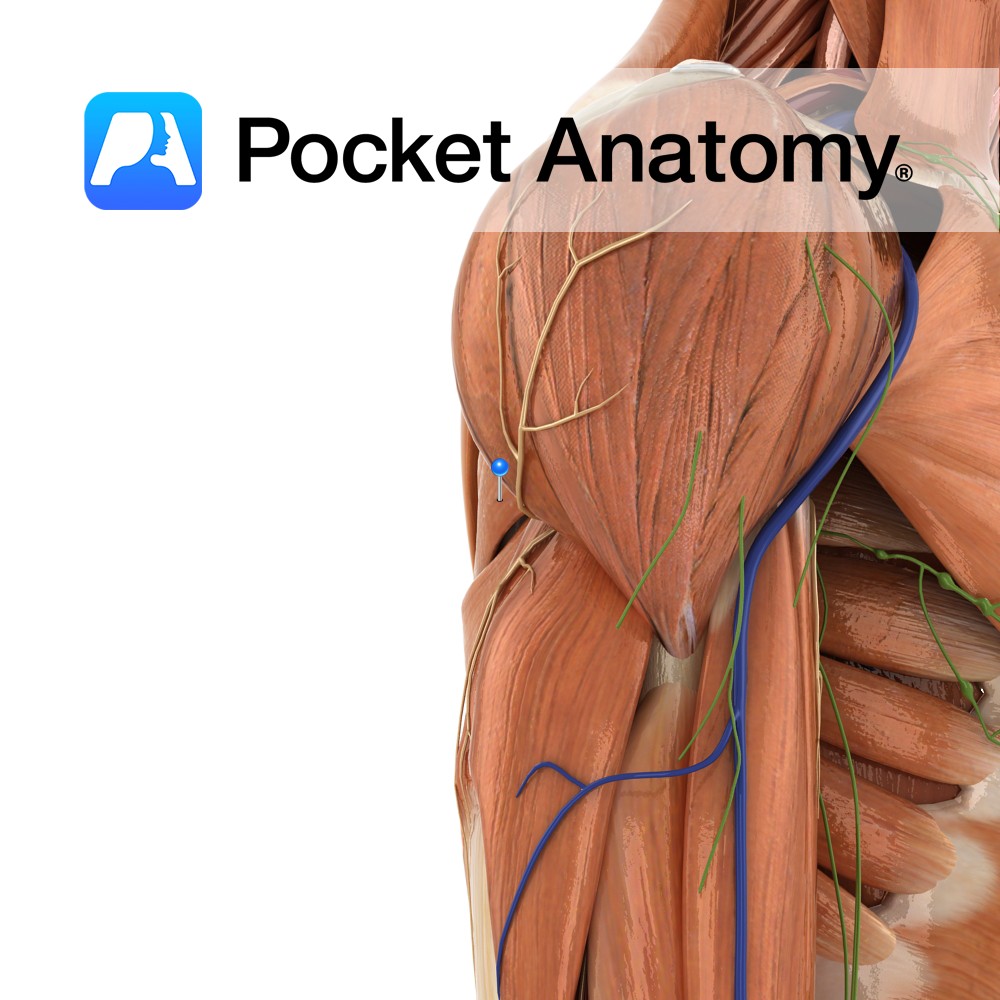
Anatomy Origin: Upper two-thirds of posterior surface of lateral border of scapula. Insertion: Inferior facet of greater tubercle of humerus. Key Relations: -The tendon of the muscle passes across and is united with the posterior capsule of the shoulder joint. -One of the four muscles of the rotator cuff muscle group. Functions -Lateral rotation of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
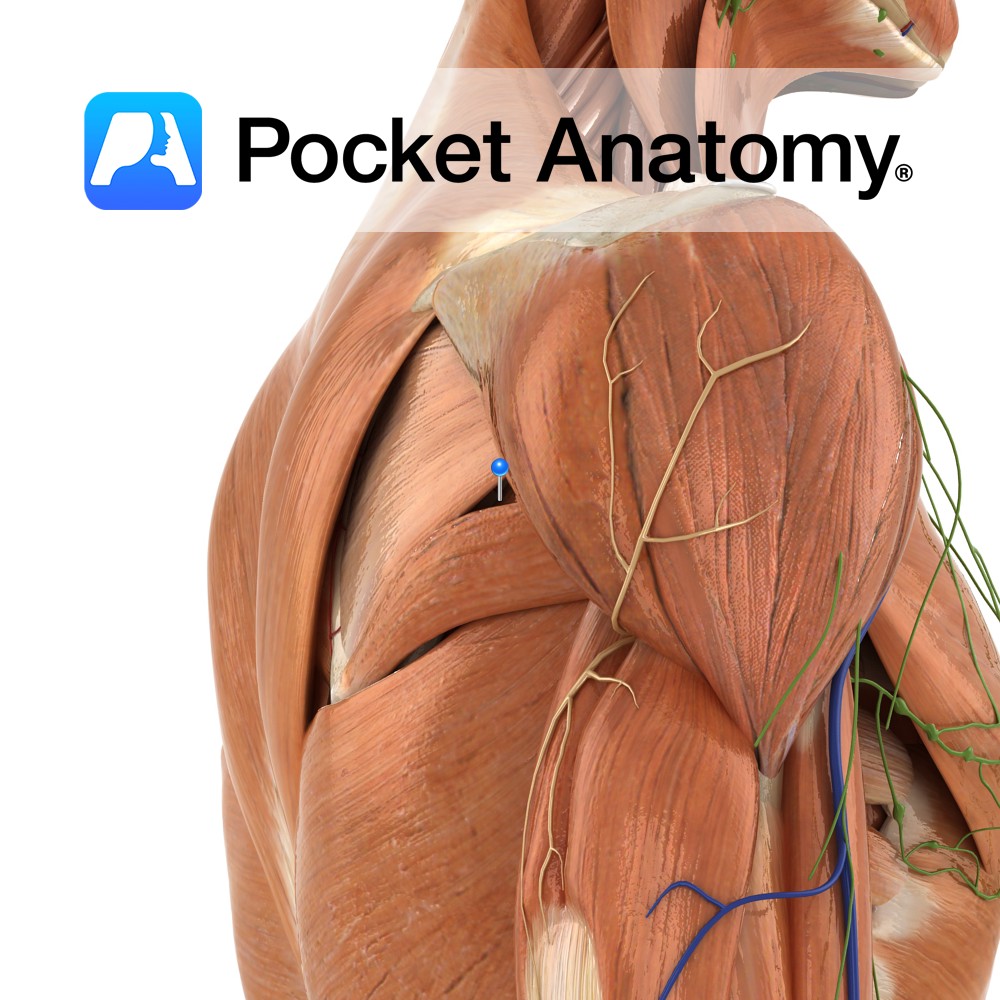
Anatomy Origin: Oval area on posterior surface of inferior angle of scapula. Insertion: Medial lip of intertubercular sulcus on anterior surface of humerus. Key Relations: The teres minor and teres major muscles form the axillary space, through which several important arteries and veins pass. Functions -Medial rotation of the arm at the glenohumeral joint. -Adduction
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Lateral aspect of anterior superior iliac spine, anterior external lip of the iliac crest and the deep surface of the fasciae latae. Insertion: Between two layers of the iliotibial band of the fascia latae ending around the mid thigh. Key Relations: -Most superficial of the anterior thigh muscles. -Lies anterior to gluteus minimus
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy This is the merging of the gastrocnemius and soleus tendons (sometimes plantaris tendon as well). It extends from the mid-calf to a smooth transverse area on the medial third of the posterior aspect of the calcaneus. Functions It is the distal tendon of the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. Clinical Achilles tendinitis and ruptures of
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Origin: Floor of temporal fossa and its overlying fascia. Insertion: Medial surface of coronoid process of mandible and anterior border of ramus of mandible. Key Relations: -Superficial to the muscle are the masseter and the temporal branches of the facial nerve. -One of the four muscles of mastication. Functions -Elevates the mandible to occlude
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
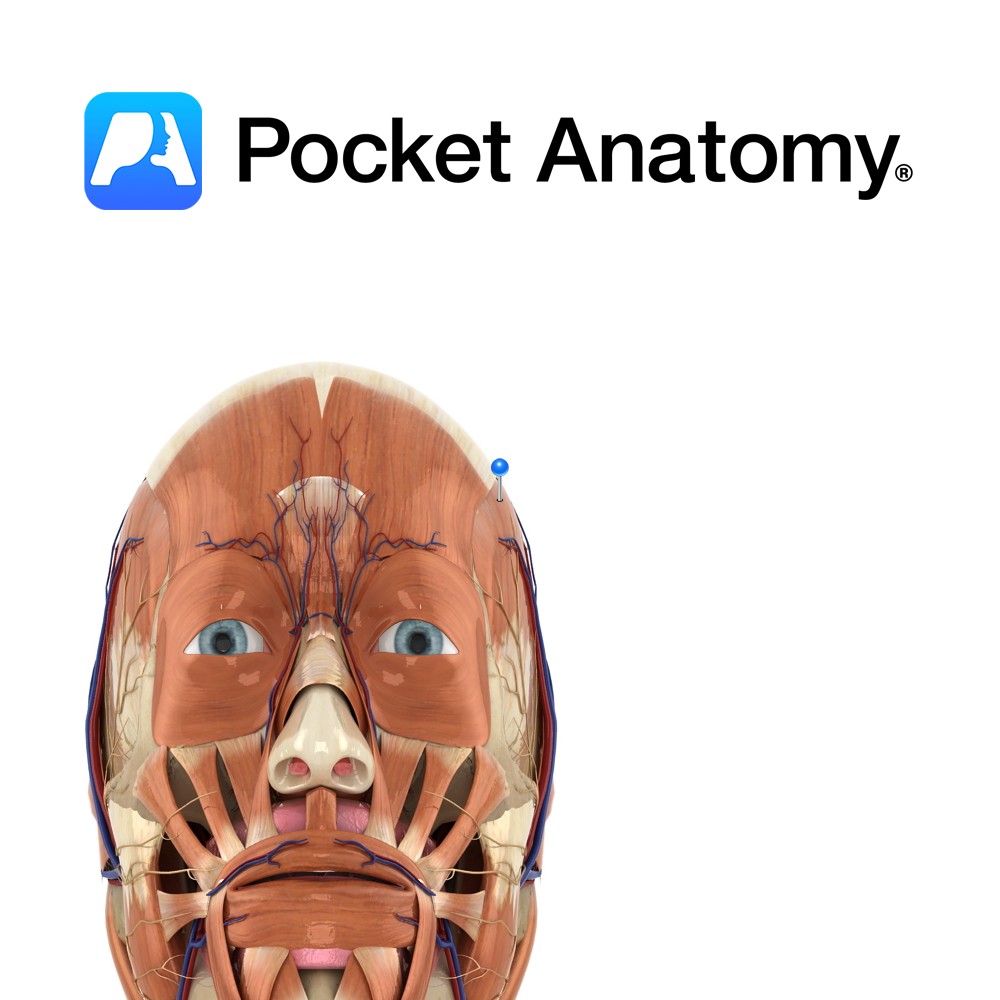
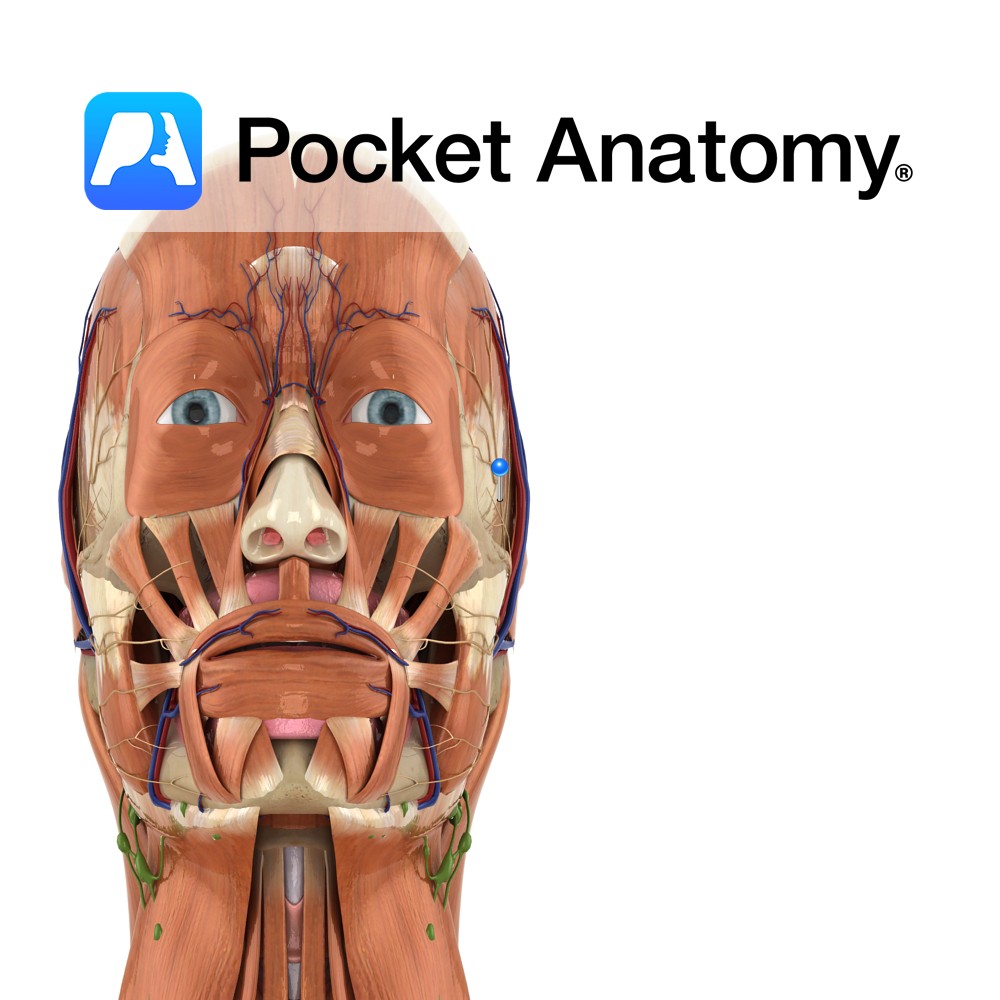
Anatomy Branch of the facial nerve (also known as the seventh cranial nerve). Facial nerve: Has a motor and sensory origin that join together to form the nerve. It passes through the internal auditory meatus through the facial canal and finally exits from the stylomastoid foramen, and into the parotid gland where it divides into
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
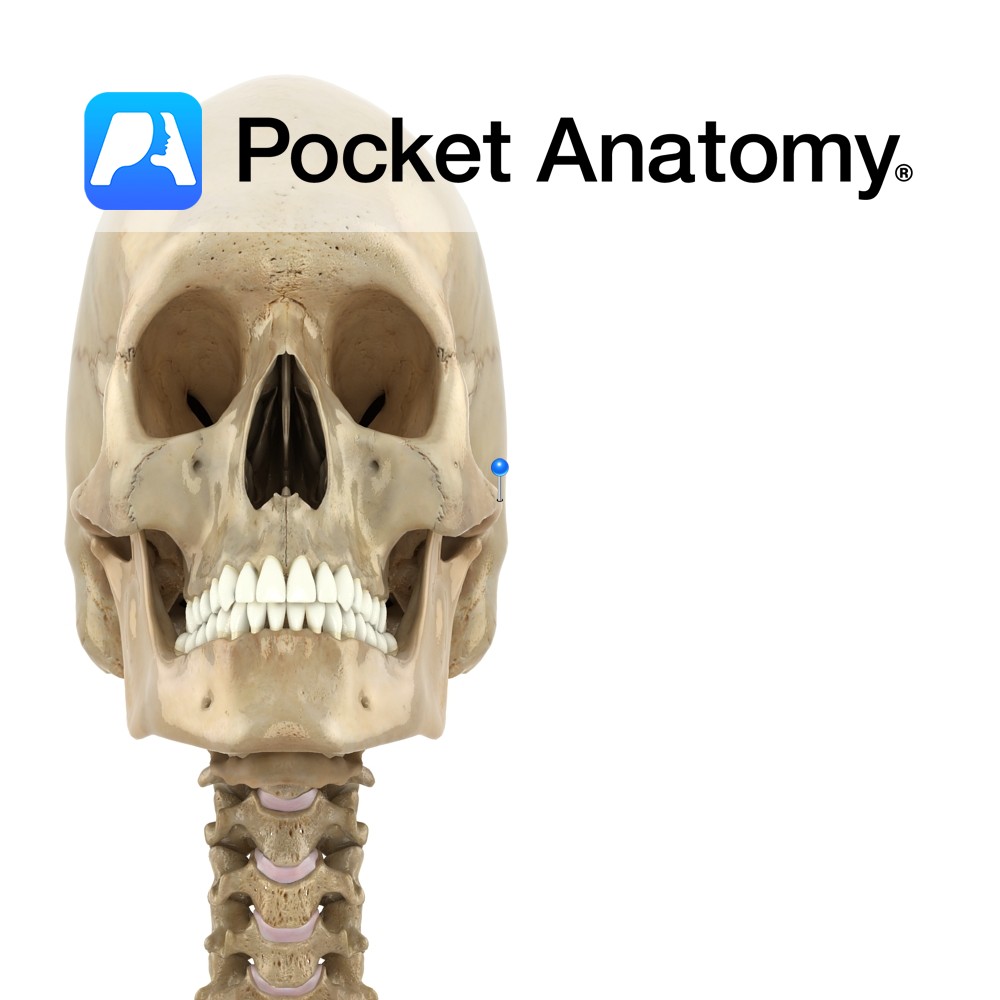
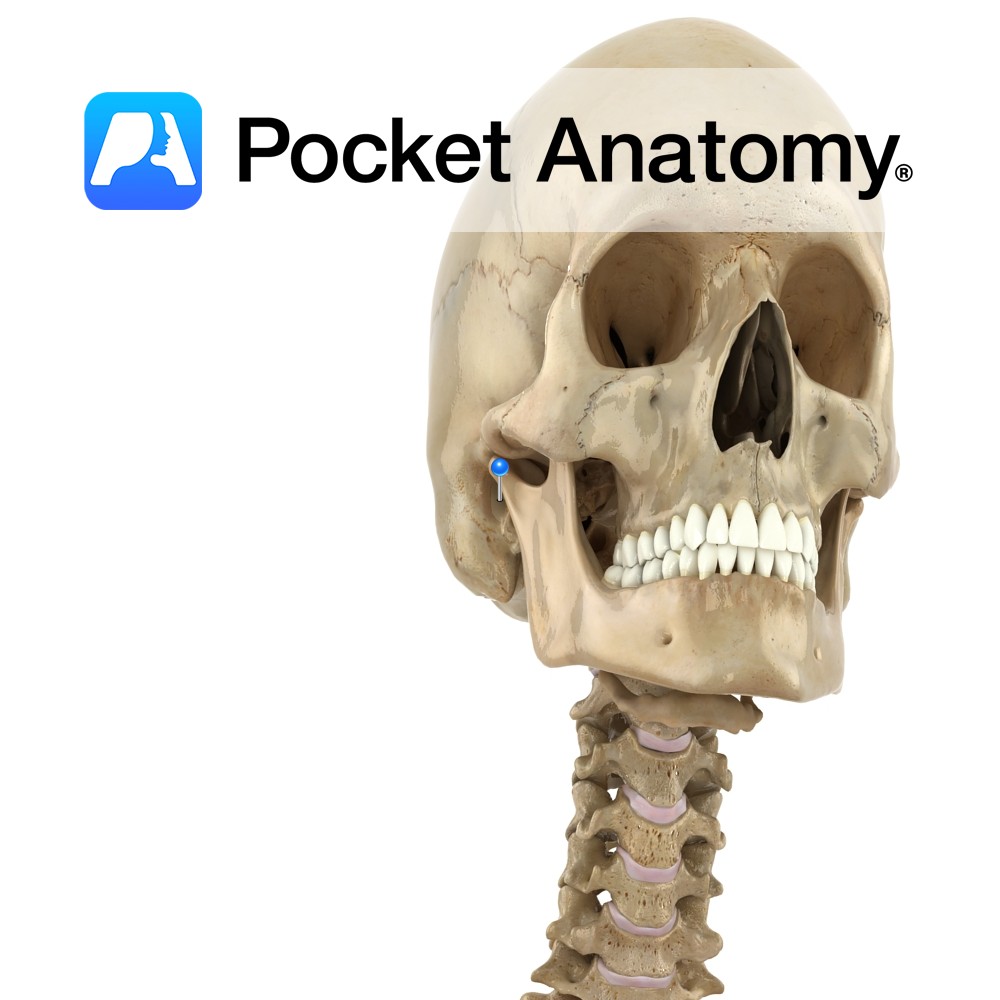
Anatomy An arched process out and forward from temporal bone. Forms an arch at side of skull with the temporal process of the zygomatic bone, in which the upper extremity of the ramus of the mandible inserts (its condylar head at the back contributing to the TMJ, and its coronoid process at the front taking
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
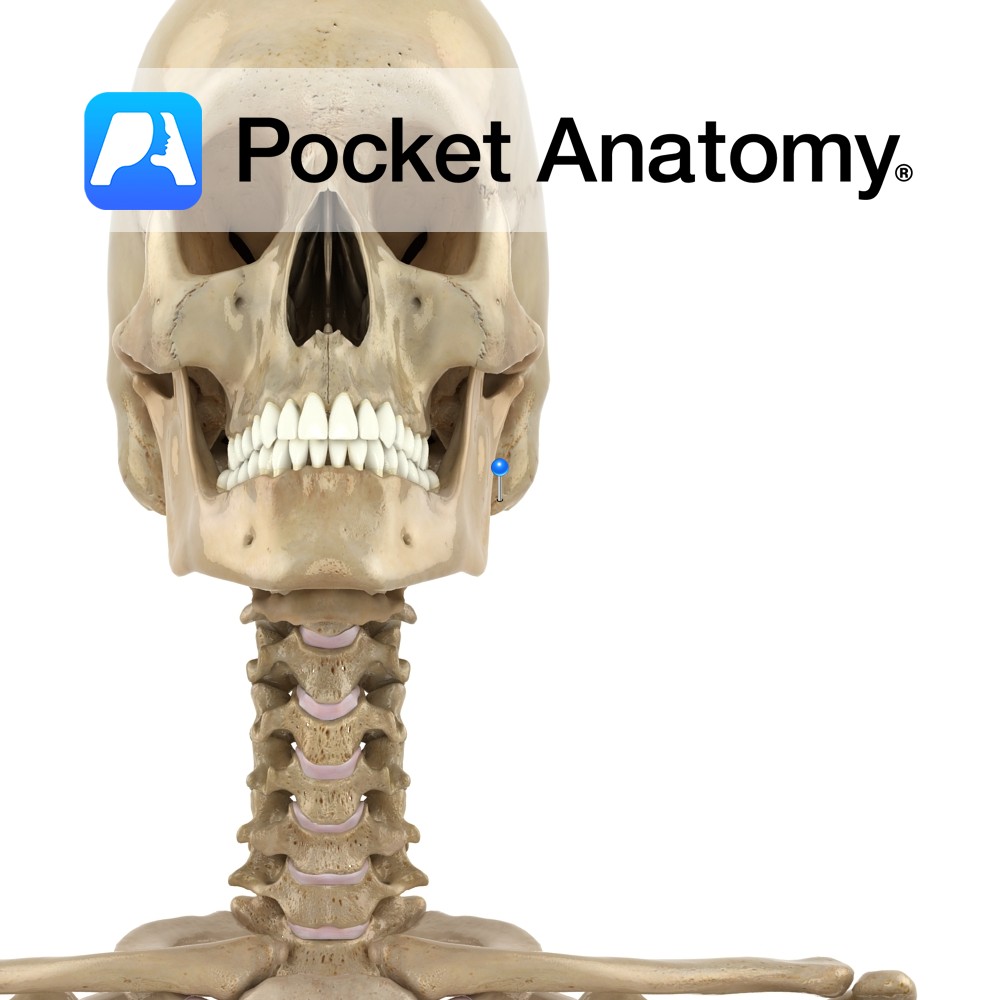
Anatomy Conical bulge from bottom surface, just behind and below external acoustic meatus. Contains small interconnected air cells/sinuses, which connect with middle ear; secrete mucus, buffer air pressure changes at eardrum. Muscles attached; splenius and longissimus capitis, digastric, sternocleidomastoid. Vignette Mastoid, ie breast-shaped. Easily felt just behind earhole, medial to pinna. Mastoiditis usually an extension
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
Anatomy Also known as the ear canal, connecting (runs forward and down) outer (pinna) to middle ear (outer 1/3 fibrocartilage, inner 2/3 bony). Clinical Common site for infection, foreign bodies. Cerumen (ear wax) lubricates, offers some protection against infection and insects. Interested in taking our award-winning Pocket Anatomy app for a test drive?
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins
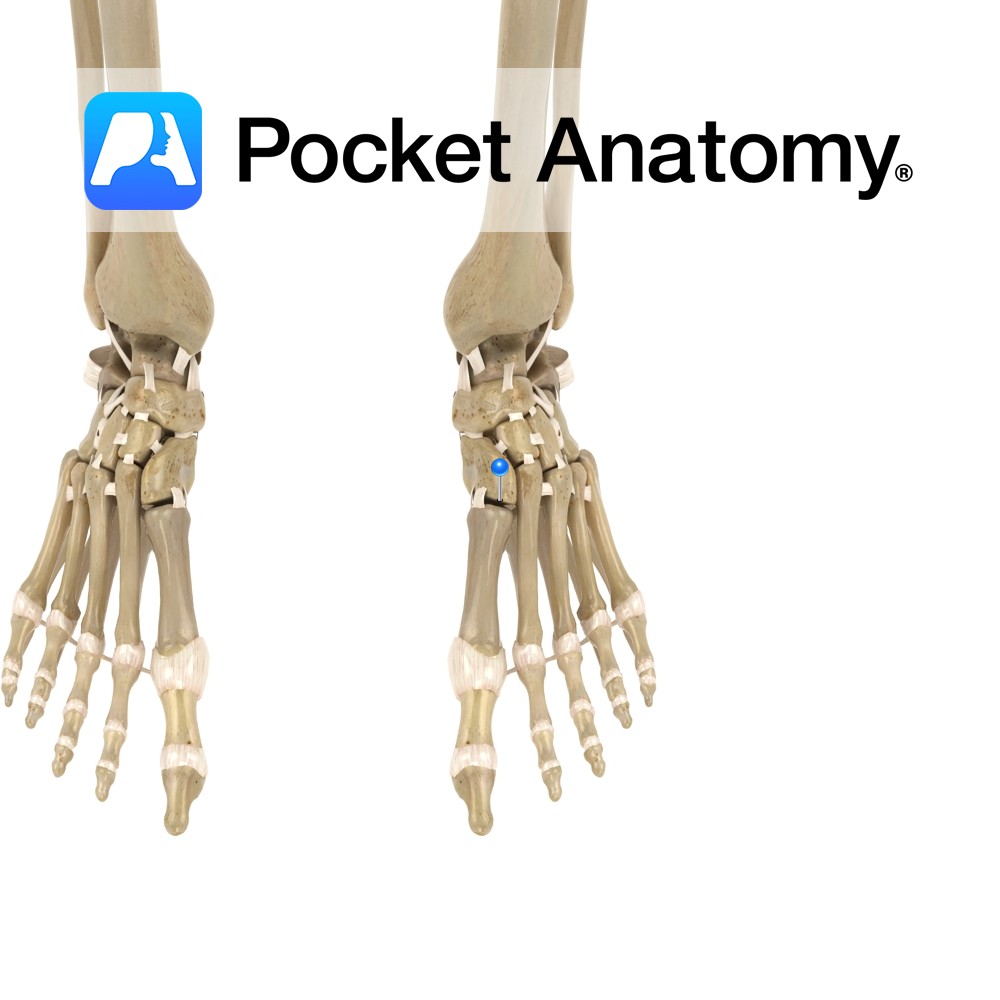
Motion The tarsometatarsal joints are synovial plane joints found in the foot. They are formed by the articulations between the five metatarsal bones and the cuneiform and cuboid bones. The 1st metatarsal articulates with the medial cuneiform, the 2nd with the intermediate cuneiform, the 3rd with the lateral cuneiform, the 4th with the lateral cuneiform
- Published in Pocket Anatomy Pins

.jpg)